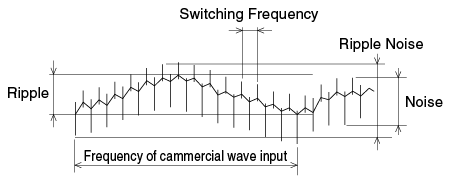
Ripple and noise refer to the unwanted AC components superimposed on a DC power supply's output. This is often specified as PARD (Periodic and Random Deviation). Total output noise is a combination of periodic ripple and random, high-frequency noise.
Switching power supplies generate high-frequency noise due to the rapid switching action of transistors and rectifiers. The figure below illustrates the relationship between ripple, noise, and total ripple noise.
In contrast, series regulators (linear power supplies) lack high-frequency switching components and therefore exhibit significantly lower noise. Their output noise is primarily composed of ripple at the commercial line frequency and its harmonics.
Related Technical Articles
- What is a Power Supply? Types and Applications
- What is a Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Safety and Usage of High Voltage Power Supply
- An Introduction to DC Power Supplies
- What is a Bipolar Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Electronic Loads: An Introduction to Principles, Types, and Uses
- What is an AC Power Source? - Basic Knowledge -
- Linear vs. Switching Power Supplies: Key Differences Explained
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies
- High Voltage Measurement Method
- How to Choose a DC Power Supply: Key Points to Consider
- Difference between DC power and AC power
- A Beginner's Guide to Using Power Supplies Safely
- A Guide to Using DC Power Supplies Correctly and Safely
- HVPS for Lab Analyzers: Key Considerations for Stability and Noise
- Amplifier Basics: Principles, Operation, and Key Considerations
- Method of Generating Direct Current (DC) Power


