Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is the ability of a device or system to function acceptably in its electromagnetic environment without introducing intolerable electromagnetic disturbances to other devices in that environment.
Say, for example, that you use a microwave in your house. The microwave can affect the wireless LAN and Bluetooth connections and cause some problems. It is a case where the microwave is causing electromagnetic interference to devices via wireless LAN or Bluetooth.
Similar cases are found when a vacuum cleaner or hair dryer is used near the TV. Many forms of electromagnetic interference may prevent regular operation. The EMC measure ensures that a variety of different items of electronic equipment can operate nearby without causing any undue interference.
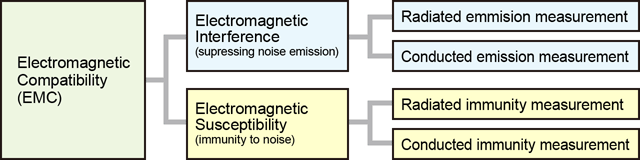
In other words, EMC comprises two key aspects: limiting its own electromagnetic emissions and having sufficient immunity to external electromagnetic disturbances.
- Emissions (or Electromagnetic Interference - EMI) refers to the generation of unwanted electromagnetic energy by a device. This energy can interfere with other nearby equipment.
- Susceptibility (or Electromagnetic Susceptibility - EMS) is the tendency of a device to malfunction when exposed to unwanted electromagnetic energy. Immunity is the opposite of susceptibility; it is a device's ability to operate correctly in the presence of such interference.
Nowadays, many things are electronic, and many wirelessly connected electronic devices operate simultaneously. EMC is of increasing importance.
Related Technical Articles
- What is a Power Supply? Types and Applications
- What is a Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Safety and Usage of High Voltage Power Supply
- An Introduction to DC Power Supplies
- What is a Bipolar Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Electronic Loads: An Introduction to Principles, Types, and Uses
- What is an AC Power Source? - Basic Knowledge -
- Linear vs. Switching Power Supplies: Key Differences Explained
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies
- High Voltage Measurement Method
- How to Choose a DC Power Supply: Key Points to Consider
- Difference between DC power and AC power
- A Beginner's Guide to Using Power Supplies Safely
- A Guide to Using DC Power Supplies Correctly and Safely
- HVPS for Lab Analyzers: Key Considerations for Stability and Noise
- Amplifier Basics: Principles, Operation, and Key Considerations
- Method of Generating Direct Current (DC) Power


