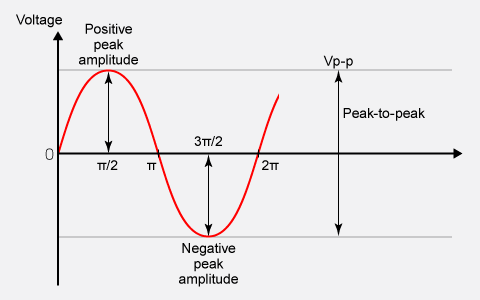
Peak-to-peak (often abbreviated as p-p or Vpp) is the difference between the maximum (positive peak) and minimum (negative peak) value of a periodic waveform.
This value quantifies the total swing of a signal and is a fundamental parameter in electronics and signal processing, especially for characterizing alternating current (AC) signals. While "amplitude" often refers to the peak amplitude (from zero to a peak), the peak-to-peak value measures the full extent from the minimum to the maximum peak.
For a symmetric waveform centered around zero, such as the sine wave shown, the peak-to-peak value is exactly twice the peak amplitude. Consequently, the peak amplitude is half of the peak-to-peak value.