In the context of power supplies, "4-quadrant" refers to the four possible operating modes defined by the polarity (positive or negative) of the output voltage and current. These modes are typically visualized on a voltage-current (V-I) graph, where the vertical axis represents voltage and the horizontal axis represents current. This creates four distinct operating regions:
- Quadrant 1 (Source): Positive Voltage, Positive Current (+V, +I)
- Quadrant 2 (Sink): Positive Voltage, Negative Current (+V, -I)
- Quadrant 3 (Source): Negative Voltage, Negative Current (-V, -I)
- Quadrant 4 (Sink): Negative Voltage, Positive Current (-V, +I)
Power supplies are classified by the number of quadrants in which they can operate.
- Single-quadrant (or one-quadrant) power supplies typically operate only in Quadrant 1, sourcing power with a positive voltage and current.
- Two-quadrant power supplies can both source and sink power. For example, a device operating in Quadrants 1 and 2 can source (+I) and sink (-I) current, both at a positive voltage.
- Four-quadrant power supplies can operate in all four quadrants.
In a high-voltage power supply, the positive output power supply in the first quadrant and the negative output power supply in the third quadrant are different products. In other words, it is important to note whether it is a positive or negative power supply. A low-voltage DC power supply can be used to switch between the first and third quadrants depending on whether the positive or negative pole is grounded.
A two-quadrant device is often called a bidirectional power supply. When such a power supply has the ability to return the absorbed (sunk) energy back to the AC power line, it is specifically referred to as a regenerative power supply.
A power supply that covers all four quadrants is known as a bipolar power supply. It can seamlessly transition between sourcing (acting as a power supply) and sinking (acting as an electronic load) for both positive and negative polarities of voltage and current.
A key advantage of bipolar power supplies is their high-speed response and ability to output a seamless waveform that transitions through zero without discontinuity. This makes them ideal for use as fast-slewing power amplifiers. Their four-quadrant capability allows them to effectively drive reactive loads (capacitive or inductive). Common applications include high-frequency ripple simulation tests for capacitors and impedance measurements.
SOURCE:The direction of voltage and current is same(supply). SINK:The direction of voltage and current is opposite(absorption).
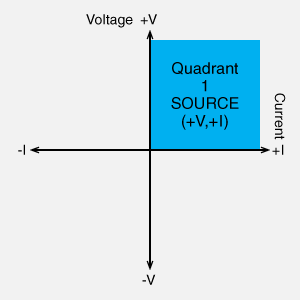
Unipolar DC power supply, Positive polarity High Voltage Power Supply
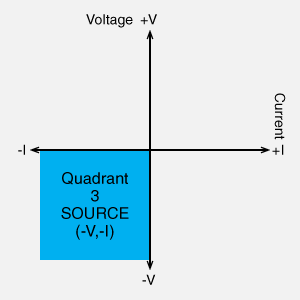
Unipolar DC power supply, Negative polarity High Voltage Power Supply
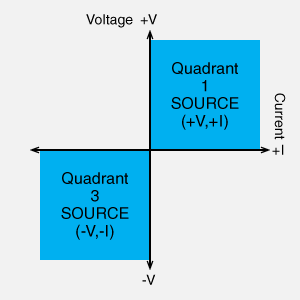
AC power source, Reversible polarity high voltage power supply (Auto-reversing high voltage power supply), Dual polarity dc power supply
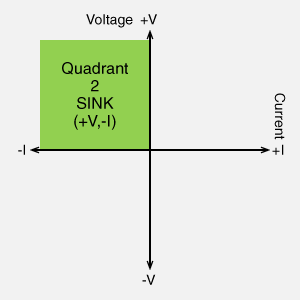
DC electronic load
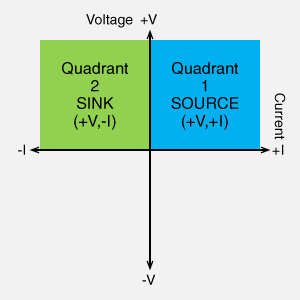
Bidirectional DC Power Supplies (Regenerative DC Power Supplies), Battery Cycle Tester
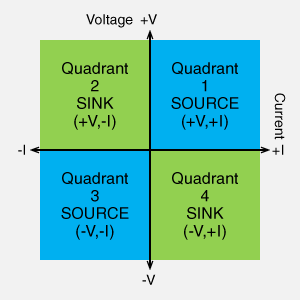
Four-quadrant bipolar power supply, bipolar Amplifier, High Voltage Amplifier














