Efficiency is the ratio of useful power output to total power input. It is a key performance indicator for a wide range of electrical equipment, such as transformers, motors, lighting, and generators. There are two primary methods for determining efficiency: direct efficiency, which is found by directly measuring the input and output power, and conventional efficiency (also known as commercial efficiency), which is calculated from the sum of individual component losses using a standardized formula.
Conventional efficiency is often used for large transformers and equipment where direct measurement of overall efficiency is impractical. For power supply units, including switching power supplies, efficiency is typically determined by direct measurement of input and output power at the rated output.
Factors contributing to inefficiency in power supplies include the ON-resistance of switching devices, switching losses, losses in diodes, winding resistance in transformers, hysteresis losses in magnetic cores, losses in capacitors, and power consumed by control circuits. Most power supplies achieve their maximum efficiency near their rated output, typically between 70% and 90% of the full load.
Operating at reduced output voltage and current lowers the input power, but this typically results in lower efficiency, especially at light loads.
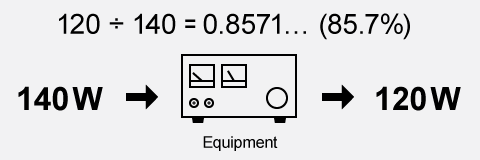
For example, if a power supply has a rated output of 12V and 10A (which is 120W of output power) and consumes 140W of input power, its efficiency is calculated as: Output Power / Input Power = 120W / 140W = 0.8571..., or 85.7%.
| losses | no-load losses | Iron or core losses | Hysteresis losses |
|---|---|---|---|
| eddy current losses | |||
| load losses | copper losses | ||
| Stray losses | |||
Related Technical Articles
- What is a Power Supply? Types and Applications
- What is a Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Safety and Usage of High Voltage Power Supply
- An Introduction to DC Power Supplies
- What is a Bipolar Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Electronic Loads: An Introduction to Principles, Types, and Uses
- What is an AC Power Source? - Basic Knowledge -
- Linear vs. Switching Power Supplies: Key Differences Explained
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies
- High Voltage Measurement Method
- How to Choose a DC Power Supply: Key Points to Consider
- Difference between DC power and AC power
- A Beginner's Guide to Using Power Supplies Safely
- A Guide to Using DC Power Supplies Correctly and Safely
- HVPS for Lab Analyzers: Key Considerations for Stability and Noise
- Amplifier Basics: Principles, Operation, and Key Considerations
- Method of Generating Direct Current (DC) Power


