Relative humidity (RH) represents the ratio of water vapor currently present in the air relative to the maximum amount the air can hold at a specific temperature (saturation). It is expressed as a percentage. In general industrial contexts, the term "humidity" typically refers to relative humidity. Measurement standards are often defined by industrial standards such as JIS Z 8806.
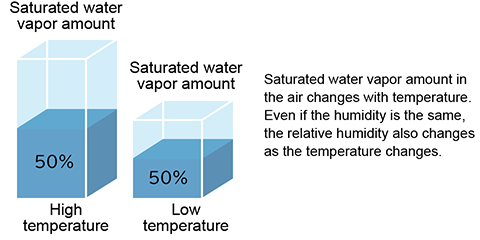
The maximum water vapor capacity of air is temperature-dependent. Consequently, relative humidity fluctuates with temperature changes, even if the absolute moisture content in the air remains constant.
Absolute vs. Relative Humidity
Another method for measuring moisture is Absolute Humidity, which represents the actual mass of water vapor per unit volume of air, typically expressed in grams per cubic meter (g/m3). Unlike relative humidity, absolute humidity does not change with temperature fluctuations, provided the moisture content remains constant.
Importance for Electronic Equipment
Relative humidity is a critical metric for environmental control in manufacturing and inspection facilities. While absolute humidity measures the mass of water, relative humidity is more relevant for assessing the risk of condensation and static electricity.
- High Humidity: Increases the risk of condensation, which can affect product quality and cause short circuits in electronic components.
- Low Humidity: Increases the risk of static electricity (ESD), which can damage sensitive electronics.
Generally, a relative humidity range of 45% to 50% is considered optimal for the operation and manufacturing of electronic equipment. This range helps balance the risks of condensation and static discharge.
Related Technical Articles
- What is a Power Supply? Types and Applications
- What is a Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Safety and Usage of High Voltage Power Supply
- An Introduction to DC Power Supplies
- What is a Bipolar Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Electronic Loads: An Introduction to Principles, Types, and Uses
- What is an AC Power Source? - Basic Knowledge -
- Linear vs. Switching Power Supplies: Key Differences Explained
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies
- High Voltage Measurement Method
- How to Choose a DC Power Supply: Key Points to Consider
- Difference between DC power and AC power
- A Beginner's Guide to Using Power Supplies Safely
- A Guide to Using DC Power Supplies Correctly and Safely
- HVPS for Lab Analyzers: Key Considerations for Stability and Noise
- Amplifier Basics: Principles, Operation, and Key Considerations
- Method of Generating Direct Current (DC) Power


