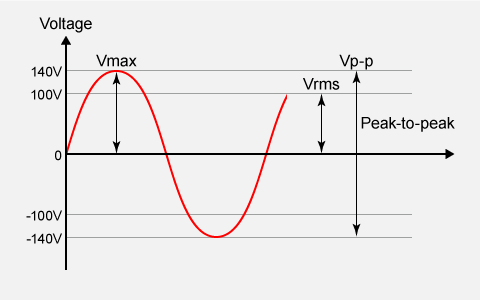
Root Mean Square (RMS) is a statistical measure used to calculate the effective value of a varying signal, such as an alternating current (AC) voltage. The RMS value represents the equivalent DC voltage that would produce the same amount of heat (power dissipation) in a resistive load.
Mathematically, RMS is the square root of the arithmetic mean of the squares of the values. For a standard continuous sine wave, the RMS value is approximately 0.707 times the peak voltage 1/
For example, if a commercial AC power line is rated at 100 Vrms, the actual peak voltage Vp reaches approximately 141 V. The difference between the positive and negative peaks is known as the peak-to-peak voltage Vpp, which in this case would be approximately 282 V.
RMS values are standard in electronics and physics for specifying AC power sources, evaluating waveform amplitudes, and performing tolerance analysis in quality control.