An equivalent circuit is a theoretical model that exhibits the same voltage, current, and frequency characteristics at its terminals as a more complex, real-world circuit or device. It serves as a simplified representation, making it easier to analyze and predict the behavior of the original system.
For example, the electrical behavior of a DC motor can be modeled by an equivalent circuit combining electrical elements like resistors and inductors. In this model, mechanical properties such as rotational speed and friction are represented by analogous electrical components (e.g., friction is modeled as a resistance). This allows the entire system's characteristics to be analyzed as a purely electrical circuit.
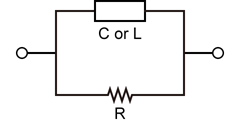
In an LCR meter, the equivalent circuit is represented using either a series equivalent circuit or a parallel equivalent circuit, and is displayed by converting the values into the parameters: inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R).
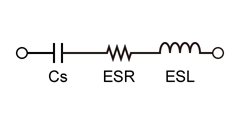
For a real-world component like a capacitor, its non-ideal properties are modeled using an equivalent circuit. The two most common models are the series equivalent circuit and the parallel equivalent circuit. The series model is particularly useful for understanding parasitic effects at high frequencies. It models a real capacitor as three ideal components in series:
- Ideal Capacitance (C): The primary, intended capacitance.
- ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance): This represents the inherent resistance of the capacitor's leads, electrodes, and dielectric material. Unlike an ideal capacitor, real capacitors have this resistance, which causes energy loss in the form of heat.
- ESI (Equivalent Series Inductance): This represents the parasitic inductance from the capacitor's leads and internal structure. This effect is negligible at low frequencies but becomes significant at high frequencies, potentially causing the capacitor to behave like an inductor.
The primary advantage of using an equivalent circuit is simplification. By representing a complex system with a simplified model, engineers can more easily analyze its behavior and perform calculations that would otherwise be intractable.
Furthermore, this concept extends beyond electronics. Physical phenomena such as mechanical vibration, heat transfer, and acoustics can be modeled using analogous electrical circuits. This powerful analysis technique is applied in diverse fields, from creating impedance models of biological tissue to designing control systems for machinery.
Related Technical Articles
- What is a Power Supply? Types and Applications
- What is a Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Safety and Usage of High Voltage Power Supply
- An Introduction to DC Power Supplies
- What is a Bipolar Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Electronic Loads: An Introduction to Principles, Types, and Uses
- What is an AC Power Source? - Basic Knowledge -
- Linear vs. Switching Power Supplies: Key Differences Explained
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies
- High Voltage Measurement Method
- How to Choose a DC Power Supply: Key Points to Consider
- Difference between DC power and AC power
- A Beginner's Guide to Using Power Supplies Safely
- A Guide to Using DC Power Supplies Correctly and Safely
- HVPS for Lab Analyzers: Key Considerations for Stability and Noise
- Amplifier Basics: Principles, Operation, and Key Considerations
- Method of Generating Direct Current (DC) Power


