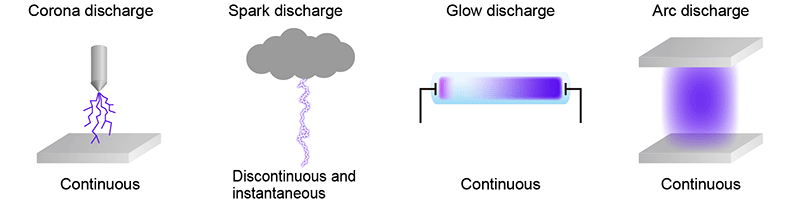
Arc discharge (or an electric arc) is an electrical discharge characterized by high current density at a low voltage. It is a self-sustaining discharge, typically maintained by the thermionic emission of electrons from a high-temperature cathode.
There are two primary types of arc discharge: hot cathode and cold cathode. In a hot cathode arc discharge, the cathode is heated to a high temperature, causing it to emit a large number of electrons through thermionic emission, which sustains the arc.
Hot cathode arc discharge is used to generate plasma for fluorescent lamps, xenon lamps, metal hydride lamps, mercury lamps, and other light sources, as well as thermal plasma and plasma torches.
Conversely, in a cold cathode arc discharge, electrons are extracted from the cathode surface by an intense electric field (a process known as field electron emission). It is important to distinguish this from glow discharge, a different phenomenon used in cold-cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs).
A common application of arc discharge is in fluorescent lighting. In these lamps, thermally emitted electrons collide with mercury atoms within the tube, causing them to emit ultraviolet (UV) light. This UV light then excites the phosphor coating on the inside of the tube, which in turn fluoresces to produce visible light.
Arc discharge is also utilized in industrial processes like arc welding and electrical discharge machining (EDM). However, due to the extremely high temperatures involved, these applications carry significant risks. Matsusada Precision offers specialized high-voltage power supplies and arc control solutions designed to manage and prevent unwanted arc discharges.
Related Technical Articles
- What is a Power Supply? Types and Applications
- What is a Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Safety and Usage of High Voltage Power Supply
- An Introduction to DC Power Supplies
- What is a Bipolar Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Electronic Loads: An Introduction to Principles, Types, and Uses
- What is an AC Power Source? - Basic Knowledge -
- Linear vs. Switching Power Supplies: Key Differences Explained
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies
- High Voltage Measurement Method
- How to Choose a DC Power Supply: Key Points to Consider
- Difference between DC power and AC power
- A Beginner's Guide to Using Power Supplies Safely
- A Guide to Using DC Power Supplies Correctly and Safely
- HVPS for Lab Analyzers: Key Considerations for Stability and Noise
- Amplifier Basics: Principles, Operation, and Key Considerations
- Method of Generating Direct Current (DC) Power


