Grounding (or earthing) is the practice of connecting an electrical circuit or equipment to the Earth via a conductive path. There are three types of grounding: safety grounding, functional grounding, and lightning protection grounding.
It is important to distinguish "common" (or "common ground") from "ground." "Common" refers to the reference potential for a circuit's operation, which is not necessarily connected to the Earth.
Safety grounding (also known as protective grounding) is an essential safety measure that protects users and equipment from electric shock by providing a path for fault currents, such as those from leakage or ground faults, to flow safely to the ground. This ensures safety by directing the fault current to the ground. In Japan, there are four Classes of safety grounding: Class A, B, C, and Class D. They are classified according to voltage and application.
Functional grounding is used to ensure the stable operation of electrical equipment. It establishes a reference potential (often considered zero volts) and can serve as a return path for signals, which helps to stabilize circuit performance and reduce noise.
Lightning protection grounding is designed to safely divert the massive current from a lightning strike to the Earth, typically via a lightning rod. The immense energy of a lightning strike can destroy equipment and buildings and is extremely dangerous to people. Properly diverting this current to the ground is crucial for protecting electrical and information systems from damage.

Under IEC standards, three types of terminals are defined in relation to grounding: the Earth (ground) terminal, the Protective conductor terminal, and the Frame or chassis terminal. Their meanings and differences are as follows.
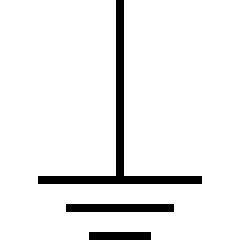 |
IEC 60417-5017 | Earth (ground) terminal: | This symbol indicates the grounding connection point of the equipment. |
 |
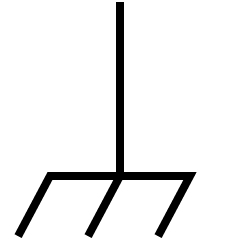
IEC 60417-5019 | Protective conductor terminal: | This symbol identifies a terminal for connecting an external protective conductor to protect against electric shock in case of a fault. |
 |
IEC 60417-5020 | Frame or chassis terminal: | This terminal is for connecting to the equipment's frame or chassis. |
Related Technical Articles
- What is a Power Supply? Types and Applications
- What is a Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Safety and Usage of High Voltage Power Supply
- An Introduction to DC Power Supplies
- What is a Bipolar Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Electronic Loads: An Introduction to Principles, Types, and Uses
- What is an AC Power Source? - Basic Knowledge -
- Linear vs. Switching Power Supplies: Key Differences Explained
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies
- High Voltage Measurement Method
- How to Choose a DC Power Supply: Key Points to Consider
- Difference between DC power and AC power
- A Beginner's Guide to Using Power Supplies Safely
- A Guide to Using DC Power Supplies Correctly and Safely
- HVPS for Lab Analyzers: Key Considerations for Stability and Noise
- Amplifier Basics: Principles, Operation, and Key Considerations
- Method of Generating Direct Current (DC) Power


