Rating can be seen in equipment specifications and performance features under certain conditions. The power supply ratings are provided for voltage, current, frequency, output, load, etc. Absolute maximum ratings, continuous ratings, instantaneous maximum ratings, short-time ratings, etc., are also available.
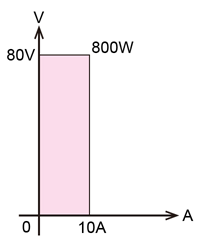
For example, in using a regulated power supply (RKT80-50 (800W)) with a rated voltage of 80 V, a rated current of 50 A, and a power consumption of 800 W, the maximum output voltage is the rated 80 V.
As the power consumption is 800W or less, up to 10 A will be available within the rating. As for the current of 50 A, the voltage is up to 16 V with 800 W limited.
Related Technical Articles
- What is a Power Supply? Types and Applications
- What is a Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Safety and Usage of High Voltage Power Supply
- An Introduction to DC Power Supplies
- What is a Bipolar Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Electronic Loads: An Introduction to Principles, Types, and Uses
- What is an AC Power Source? - Basic Knowledge -
- Linear vs. Switching Power Supplies: Key Differences Explained
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies
- High Voltage Measurement Method
- How to Choose a DC Power Supply: Key Points to Consider
- Difference between DC power and AC power
- A Beginner's Guide to Using Power Supplies Safely
- A Guide to Using DC Power Supplies Correctly and Safely
- HVPS for Lab Analyzers: Key Considerations for Stability and Noise
- Amplifier Basics: Principles, Operation, and Key Considerations
- Method of Generating Direct Current (DC) Power


