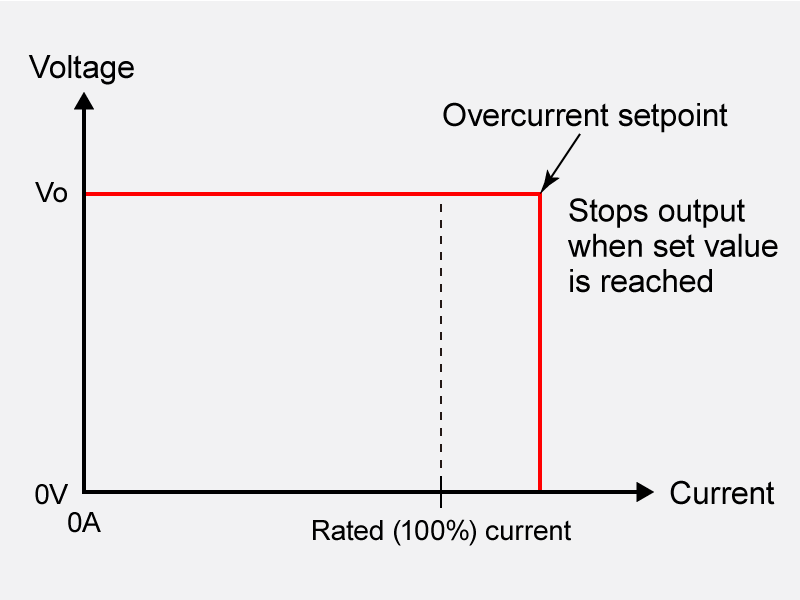
Overcurrent Protection (OCP) is a safety feature designed to protect an electronic circuit by either limiting or shutting down the output when the current exceeds a predetermined safe level. While some forms of OCP that only limit the current are known as "current limiters," the term OCP broadly covers various protective responses. It is a fundamental safety function in power supplies and other electronic devices.
Overcurrent conditions are typically caused by short circuits or excessive loads. If not properly managed, the excess current can cause overheating, leading to damage or destruction of both the power supply unit and the connected equipment (the load). OCP is essential for preventing these hazards, functioning similarly to a circuit breaker in a building's electrical system.
The recovery method after an OCP event depends on the power supply design. Some models feature auto-recovery, where the output is restored automatically once the fault condition is removed. Others may require a manual reset, such as by cycling the power. If OCP activates repeatedly, it indicates a persistent fault that must be investigated and resolved. For devices using a fuse for overcurrent protection, the blown fuse must be replaced.
FAQ: What is the response time of the protection function?