In electronics, "floating" refers to a circuit or component that is not electrically connected to a common reference potential, such as earth ground. This means the circuit is galvanically isolated, allowing its potential to be independent of the ground potential. A "floating ground" is a reference point within such an isolated circuit, acting as the 0V for that circuit, but it itself is not connected to the earth ground.
A power supply with a floating output offers significant flexibility. While it is common practice to ground one of the output terminals (either positive or negative) to establish a fixed reference, this is not a requirement for floating supplies. This capability allows the output to be used in various advanced configurations.
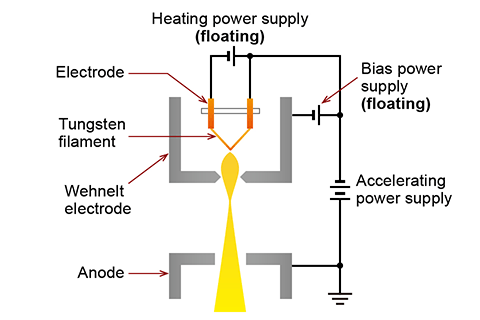
The key feature of a floating power supply is the galvanic isolation between its input and output, which is specified by an isolation voltage rating. This electrical separation enables versatile applications, such as connecting multiple power supply outputs in series to achieve higher voltages, or creating a split-rail (positive and negative) supply referenced to a local floating ground. This isolation is typically achieved using components like isolation transformers and optocouplers, which ensures both safety and the prevention of ground loops.
Related Technical Articles
- What is a Power Supply? Types and Applications
- What is a Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Safety and Usage of High Voltage Power Supply
- An Introduction to DC Power Supplies
- What is a Bipolar Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Electronic Loads: An Introduction to Principles, Types, and Uses
- What is an AC Power Source? - Basic Knowledge -
- Linear vs. Switching Power Supplies: Key Differences Explained
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies
- High Voltage Measurement Method
- How to Choose a DC Power Supply: Key Points to Consider
- Difference between DC power and AC power
- A Beginner's Guide to Using Power Supplies Safely
- A Guide to Using DC Power Supplies Correctly and Safely
- HVPS for Lab Analyzers: Key Considerations for Stability and Noise
- Amplifier Basics: Principles, Operation, and Key Considerations
- Method of Generating Direct Current (DC) Power


