Input power refers to the electrical power supplied to a power supply. Not all of this supplied power is actually consumed by the device to perform work. For this reason, it is useful to distinguish between two types of input power:
Apparent Power (VA): The total power that flows into the power supply, which is the product of the RMS input voltage and RMS input current.
Active Power (W): Also known as "real power," this is the portion of power that is actually consumed by the power supply and converted into DC output and heat.
The input stage of most power supplies includes capacitive rectification and smoothing circuits. These circuits cause the AC input current waveform to be non-sinusoidal (distorted).
While apparent power is a simple product of RMS values, active power is the integral of the instantaneous power (instantaneous voltage multiplied by instantaneous current) over one full cycle. The difference between apparent power and active power is known as reactive power. This is power that is not consumed to do work but is instead stored and discharged by reactive components (capacitors, inductors) and returned to the AC power line.
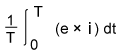
Related Technical Articles
- What is a Power Supply? Types and Applications
- What is a Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Safety and Usage of High Voltage Power Supply
- An Introduction to DC Power Supplies
- What is a Bipolar Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Electronic Loads: An Introduction to Principles, Types, and Uses
- What is an AC Power Source? - Basic Knowledge -
- Linear vs. Switching Power Supplies: Key Differences Explained
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies
- High Voltage Measurement Method
- How to Choose a DC Power Supply: Key Points to Consider
- Difference between DC power and AC power
- A Beginner's Guide to Using Power Supplies Safely
- A Guide to Using DC Power Supplies Correctly and Safely
- HVPS for Lab Analyzers: Key Considerations for Stability and Noise
- Amplifier Basics: Principles, Operation, and Key Considerations
- Method of Generating Direct Current (DC) Power


