Series operation refers to a configuration method in which power supplies are connected in a series to achieve higher output voltages.
In this configuration, the positive terminal of one supply connects to the negative terminal of the next, resulting in a total voltage equal to the sum of individual supply voltages. This follows the fundamental principle of series circuits in electrical theory, in which voltages across series-connected elements add together.
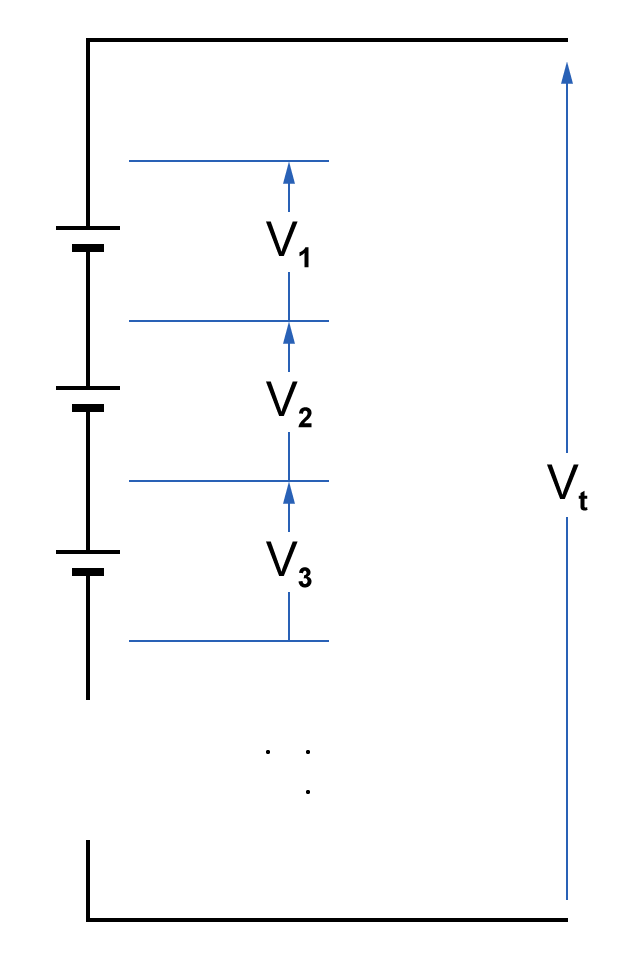
For instance, connecting two ±30 kV high-voltage power supplies in series enables the generation of ±60 kV output. This technique is frequently employed in testing equipment and research applications requiring high-voltage operation.
Several critical considerations apply to series operations. Inadequate insulation performance between power supplies increases the risk of current leakage and equipment damage. Moreover, each power supply's output typically contains minor ripple (voltage waveform fluctuations), which can accumulate in series configuration and potentially degrade overall output quality. Additionally, should any power supply fail or disconnect, remaining supplies may apply reverse voltage to the failed unit. Therefore, installing reverse voltage protection diodes in parallel with each power supply is essential.
While series operation provides an effective means of achieving high voltages, proper design considerations are crucial to ensure both safety and stability.


