Impedance is the measure of the total opposition to current flow in an alternating current (AC) circuit. It is represented by the ratio of voltage to current, and its unit is the ohm (Ω), the same as for electrical resistance. In a direct current (DC) circuit under steady-state conditions, an ideal inductor (coil) acts as a short circuit (offering no opposition to current), while an ideal capacitor acts as an open circuit, completely blocking the flow of current.
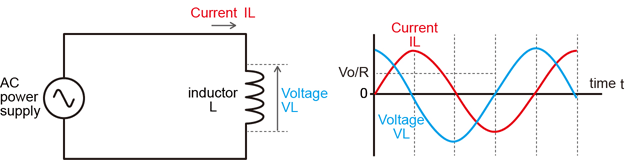
In AC circuits, components such as inductors (coils) and capacitors also oppose the flow of current, in addition to resistors. This opposition from inductors and capacitors is called "reactance." For an inductor, a changing voltage induces a magnetic field that opposes the change in current. This property is known as inductive reactance, which is a component of the total impedance.
In summary, impedance (symbolized by Z) is the complex sum of two components: resistance (R) and reactance (X). Resistance is the opposition to current that is independent of frequency. Reactance, found in inductors and capacitors, is the opposition to current that varies with frequency. Therefore, the overall impedance of a circuit is also frequency-dependent.
Related Technical Articles
- What is a Power Supply? Types and Applications
- What is a Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Safety and Usage of High Voltage Power Supply
- An Introduction to DC Power Supplies
- What is a Bipolar Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Electronic Loads: An Introduction to Principles, Types, and Uses
- What is an AC Power Source? - Basic Knowledge -
- Linear vs. Switching Power Supplies: Key Differences Explained
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies
- High Voltage Measurement Method
- How to Choose a DC Power Supply: Key Points to Consider
- Difference between DC power and AC power
- A Beginner's Guide to Using Power Supplies Safely
- A Guide to Using DC Power Supplies Correctly and Safely
- HVPS for Lab Analyzers: Key Considerations for Stability and Noise
- Amplifier Basics: Principles, Operation, and Key Considerations
- Method of Generating Direct Current (DC) Power


