A bipolar power supply is a single unit that can seamlessly output both positive (+) and negative (-) polarity voltage and current, passing smoothly through zero. The term "bipolar" means "having two poles," and as the name suggests, it can freely switch the output polarity.
Whereas a conventional DC power supply (unipolar power supply) can only supply voltage and current (a "source" function), a bipolar power supply has both this "source" capability and the ability to absorb or sink current (a "sink" function). This enables four-quadrant operation, allowing a single unit to perform the roles of four distinct devices: a DC power supply, an AC power source, an electronic load, and an amplifier. This versatility is why bipolar power supplies are used in a wide range of fields, from evaluation and testing to research and development.
High Voltage Amplifier (HV Amplifier)
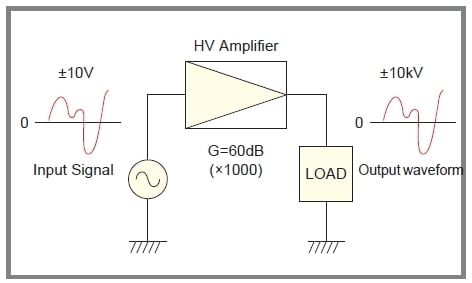
A high-voltage amplifier converts a low-voltage input signal into a high-voltage output waveform (Figure 1). Demand for these amplifiers is growing as they become indispensable tools for research, development, and system integration in fields such as electronics, physics, biochemistry, and medicine. Leveraging our advanced high-voltage technology, Matsusada Precision offers a diverse range of high-voltage amplifiers designed to meet a wide variety of customer requirements. * In addition to the models featured here, we also develop amplifiers specifically for applications such as electrostatic chucks (E-chucks) and PZT drivers. For more information, please contact our sales team.
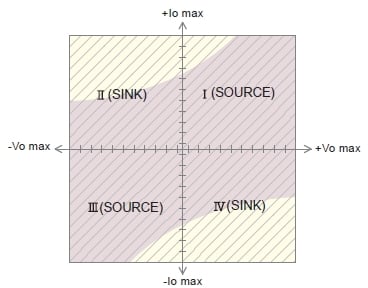
Four-Quadrant Output Range
Our high-voltage amplifiers feature a four-quadrant output, meaning they can both source (supply) and sink (absorb) current. This capability ensures stable voltage operation regardless of the load type (e.g., capacitive or inductive). Their fast response makes them ideal for applications requiring high-speed AC or arbitrary waveform outputs.
All Matsusada Precision high-voltage amplifiers (excluding some models) are bipolar, enabling true four-quadrant operation (Figure 2).
- Vomax: Rated output voltage
- Iomax: Rated output current

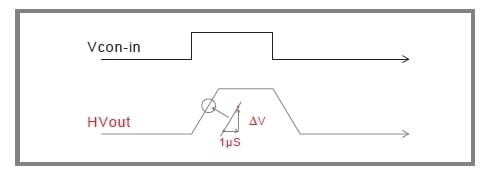
Slew Rate
The slew rate is the maximum rate of change of the output voltage and is a key indicator of an amplifier's response speed. It is expressed as dV/dt, typically in V/μs. For a given slew rate, a smaller output amplitude results in a shorter response time.
Our highest-performing AMPS series, for example, achieves a slew rate of over 1200 V/μs.
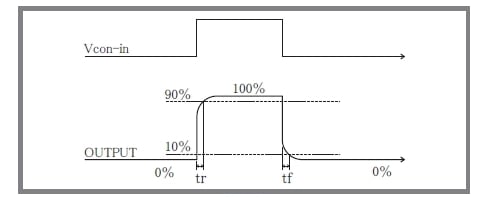
Rise Time (step response)
Step response can be indicated by the rise time, as shown in Figure 4. The rise time of an amplifier with a frequency response (= bandwidth) of fc (Hz) is typically given by the following formula.
tr ≅ 0.35/fc
The fall time (tf) is equal to tr.
Frequency Response
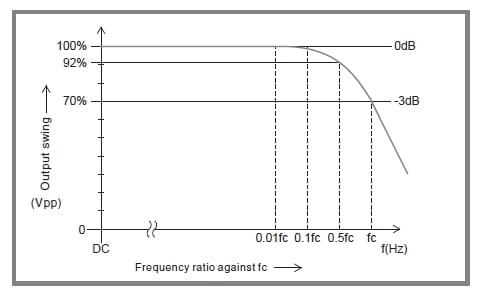
The response of Matsusada Precision amplifiers is described as "Frequency Response (Bandwidth)." When the output is driven with a sinusoidal waveform into a rated resistive load, the output swing (amplitude) decreases as the input frequency increases. In the specifications, the frequency response refers to the frequency fc at which the output swing is reduced to approximately 70.7% (-3 dB). (fig. 5)
To ensure accurate waveform reproduction, select an amplifier with a bandwidth sufficiently higher than the operating frequency.
As a rule of thumb, a bandwidth 3 to 5 times higher is recommended for sinusoidal waveforms, and at least 10 times higher for square waveforms. An insufficient bandwidth will not only reduce the output amplitude but also introduce significant phase shift. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor the output waveform to confirm it meets your application's requirements.
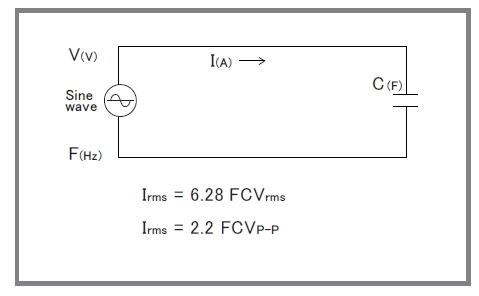
For capacitive load and discharge load
When a capacitive load of 100 pF or more (including the stray capacitance of the output wire) is connected to the power supply, the output voltage
may oscillate.
In this case, insert a high-voltage resistor of 100 Ω (at 0.1 μF) to 1000 Ω (at 1000 pF) in series with the output. Note that with a capacitive load, the frequency bandwidth is limited according to the equation on the right.
Additionally, applications involving electrical discharge, such as corona discharge, can generate excessive currents that exceed the amplifier's rating, which may cause damage. To protect the amplifier in these applications, always connect a series protection resistor to the output to limit the current.
This practice helps ensure a long product life.
Optimizing Performance: Cabling and Connections
We strongly recommend using non-shielded cables for the high-voltage output. When the output waveform is a sine wave, square wave, or other AC waveform, stray capacitance can form between the output cable and any nearby conductive objects. This capacitance leads to the flow of excess charging and discharging currents.
This additional capacitive current flows in parallel with the load, causing the following problems:
1. Reduced slew rate and response speed.
2. Distortion of the output waveform.
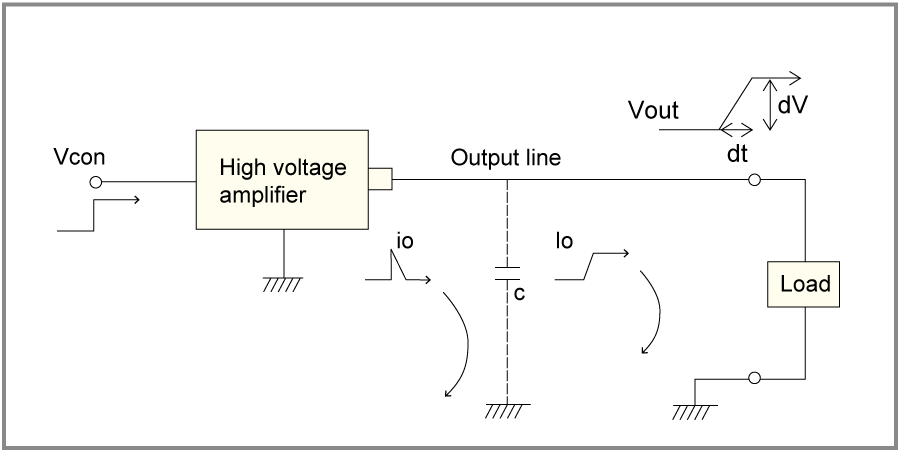
Leakage current due to stray capacitance "C" from the output cable.
Solution
Minimizing Stray Capacitance To minimize the effects of stray capacitance from the output cable:
- Keep the cable as short as possible.
- Route the cable away from any conductive surfaces such as floors, desks, or metal chassis.
- Use non-shielded high-voltage cables.
Related Technical Articles
Recommended products
Matsusada Precision has a long track record and an extensive lineup to meet your bipolar power supply or high voltage amplifier requirements.






