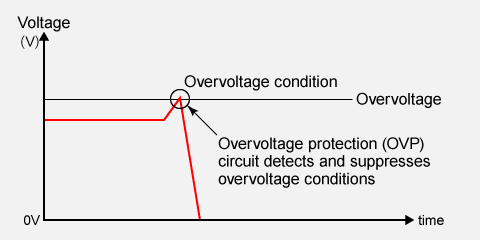
Overvoltage Protection (OVP) is a safety feature in a power supply that protects both the power supply and the connected load by shutting down the output if the voltage exceeds a predetermined safe level.
Common causes of input-side overvoltage include external events like lightning strikes or power line surges. Output-side overvoltage, however, often results from an internal failure in the power supply's regulation circuit or from an external voltage being applied to the output terminals.
Without OVP, an overvoltage event can damage or destroy sensitive electronic components such as ICs, capacitors, and resistors. In severe cases, this can lead to overheating and pose a fire hazard. Therefore, overvoltage protection is an essential feature for reliable and safe operation.
OVP is implemented using various circuit techniques. Common methods include using a comparator IC to monitor the voltage and trigger a shutdown, or employing components like Zener diodes or Transient Voltage Suppression (TVS) diodes to clamp the voltage at a safe level.
Overvoltage protection (OVP) circuits are also used in many power supply ICs and power supply devices. Many of Matsusada Precision's power supply devices are equipped with Overvoltage protection (OVP).
FAQ: How long does the protection work time?
Related Technical Articles
- What is a Power Supply? Types and Applications
- What is a Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Safety and Usage of High Voltage Power Supply
- An Introduction to DC Power Supplies
- What is a Bipolar Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Electronic Loads: An Introduction to Principles, Types, and Uses
- What is an AC Power Source? - Basic Knowledge -
- Linear vs. Switching Power Supplies: Key Differences Explained
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies
- High Voltage Measurement Method
- How to Choose a DC Power Supply: Key Points to Consider
- Difference between DC power and AC power
- A Beginner's Guide to Using Power Supplies Safely
- A Guide to Using DC Power Supplies Correctly and Safely
- HVPS for Lab Analyzers: Key Considerations for Stability and Noise
- Amplifier Basics: Principles, Operation, and Key Considerations
- Method of Generating Direct Current (DC) Power


