X-ray inspection reveals the internal structures of both devices without the need for disassembly.
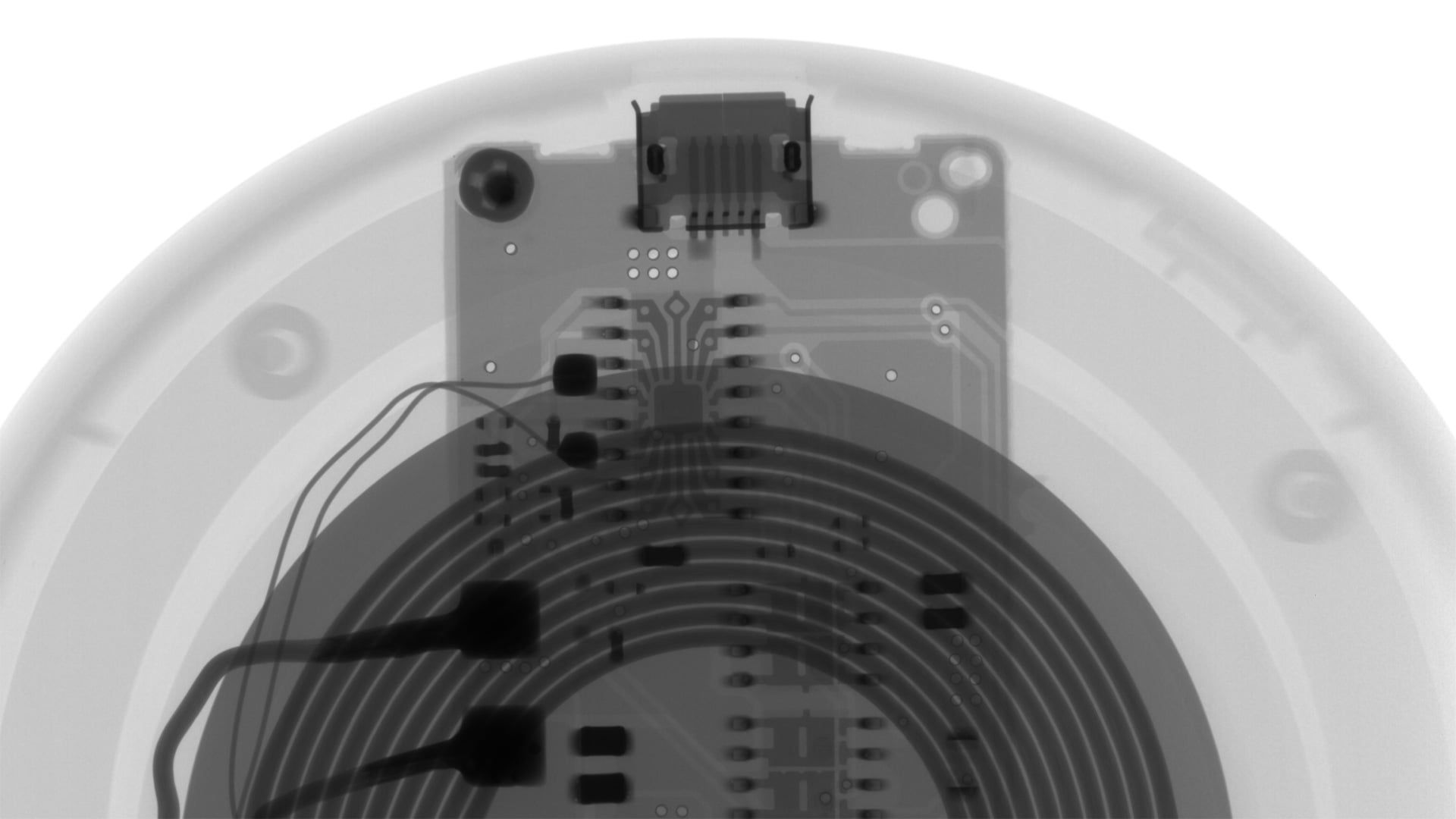
Wireless charging operates without physical connections, utilizing electromagnetic induction through coils. When current flows through the transmission coil in the charger, it generates a magnetic field. Placing a smartphone within this field induces current in the phone's receiving coil, transferring electrical power for charging. The X-ray image allows for the verification of coil alignment and winding conditions.
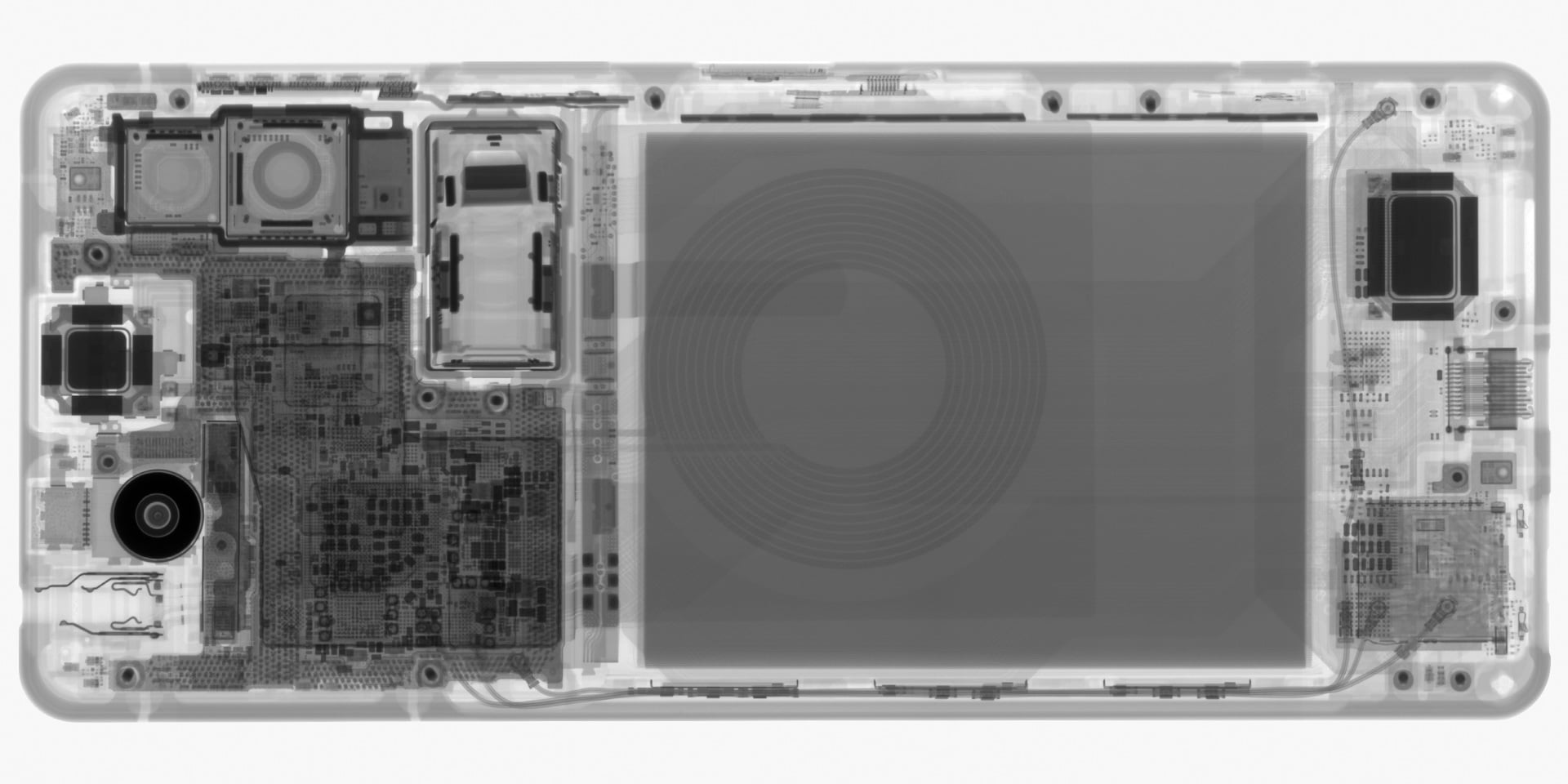
The high-resolution X-ray image captures minute details of the smartphone's internal assembly. Key components such as the camera lens, antenna, display connections, and BGA ICs are clearly visible, along with the precise layout of PCB vias and wiring patterns.
| Focal spot | Microfocus |
|---|---|
| X-ray tube voltage | 130 kV |
Recommended products
Related Technical Articles
- Selecting an X-ray Inspection System
- Principles of Radiography
- Safe Operation of X-ray Inspection Systems
- What is Microfocus X-ray Technology? (Basic Knowledge)
- Basics and Principles of Computed Tomography (CT)
- Non-Destructive Testing: Types and Applications
- What are X-rays? (Basic Knowledge)
- How to Acquire High-Quality Computed Tomography (CT) Images - X-ray NDT series (1)
- A Guide to X-ray CT Images: Formats, Viewing, and Applications - X-ray NDT series (2)
- X-ray Image Processing and Automated Inspection - X-ray NDT series (3)
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies
- What is the difference between Radioactivity, Radiation, and Radioactive Materials?
- Understanding Radiation: Effects on the Body and X-ray Safety





