
What is Non-Destructive Testing?
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) allows inspectors to collect data on a product without damaging it. It is used to detect internal defects and assess deterioration without disassembling or destroying the object.
While the terms Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) and Non-Destructive Inspection (NDI) are often used interchangeably, strictly speaking, NDT refers to the testing process itself, whereas NDI implies a pass/fail judgment based on specific standards or criteria.
Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) Z 2300 defines Non-destructive testing as "Testing to determine the presence or absence of flaws, their location, size, shape, distribution state, etc., without destroying the material or product". And Non-destructive testing is defined as "a judgment based on the non-destructive testing result according to standards or criteria.
In some cases, however, non-destructive inspection is similarly used to NDT. As the methods of the non-destructive inspection in this section also includes NDT's, we recommend separating the use depending on your applications and purposes.
The most two NDT purposes are:
- Quality Assessment :
- Checks for problems with manufactured products and parts. For example, it is used to check shrinkage cavities in casting, welding defects, etc.
- Lifetime evaluation :
- Confirms safe usage in the product operation. It is available to check for abnormalities in structures and infrastructures that will be used for a long period.
Advantages of Non-destructive Testing
Non-destructive testing offers safe and effective ways of inspecting objects as follows.
- High accuracy, easy to find defects that cannot be seen from the surface.
- No damage to objects, available for all inspection.
- Increasing product reliability
- Identify timely repair or replacement
The non-destructive testing is particularly accurate effective because it can identify internal defects of the objects without destroying them. The method is the same as an X-ray examination that shows broken parts that are difficult to discern externally.
The NDT is available for the inspection of products before shipment since the method does not contaminate or damage them. This makes it helpful in ensuring better-inspected products by all inspections, increasing product reliability. In some cases of the NDT, however, you might require many preparation processes that are relatively expensive.
Common NDT Methods
Several techniques are used in non-destructive testing, selected based on the material properties and the type of defects being inspected.
| Internal defect | RT : Radiographic Testing |
|---|---|
| UT : Ultrasonic Testing | |
| Surface defect ET : Electromagnetic (Eddy Current) Testing | ET : Electromagnetic (Eddy Current) Testing |
| MT : Magnetic Particle Testing | |
| Surface opening defect | PT : Penetrant Testing |
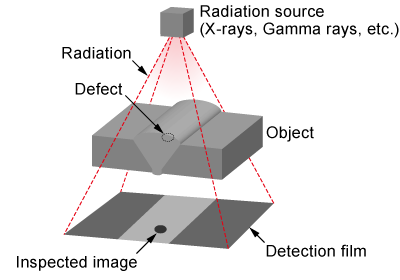
Radiographic Testing (RT)
Radiographic testing (RT) uses X-rays or gamma rays to penetrate objects. By analyzing differences in material thickness and density appearing in the images, RT detects internal defects. Computed Tomography (CT) is an advanced imaging method providing cross-sectional and 3D images, allowing for detailed analysis of internal structures.
Note: As RT utilizes radiation, appropriate safety measures and strict adherence to regulations are required during operation.
Applications: Internal analysis of lithium-ion batteries and PCBs; inspection of pipes and welds in power plants and infrastructure.
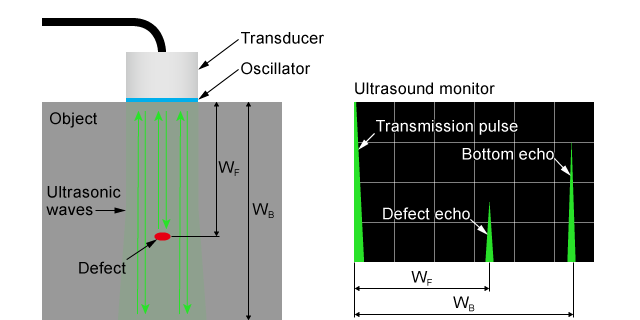
Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
Ultrasonic testing (UT) transmits ultrasonic waves into an object. By measuring the reflection of sound waves from internal boundaries or anomalies, UT inspects the internal condition of the material. It is a safe and widely used method for detecting internal flaws in homogeneous materials.
Limitations: Inspecting irregularly shaped materials or rough surfaces can be difficult.
Applications: Detecting internal defects in rolled metal products and composite materials.
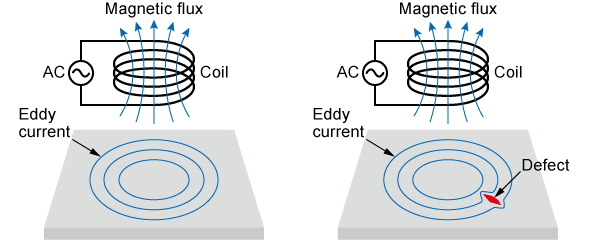
Eddy Current Testing (ET)
In Eddy Current Testing (ET), a coil carrying an AC current is placed near the object's surface. This induces eddy currents within the conductive material. Disruptions in the eddy current flow caused by surface cracks or defects are then measured. ET is ideal for automated inspections as it typically requires no surface preparation.
Limitations: ET is only effective on conductive materials.
Applications: Surface crack detection, thickness measurements, and manufacturing line inspections.
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT)
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT) is used to detect defects just beneath the surface of materials in an inspection solution containing magnetic powder. An electric current is applied to the object to inspect it by changing the magnetic powder pattern on the object's surface. When the current encounters defects there, it will create a flux leakage field where the defect is located.
It is used to detect shallow/fine cracks in a surface, and it is available for aircraft, automobile, and railroad parts.
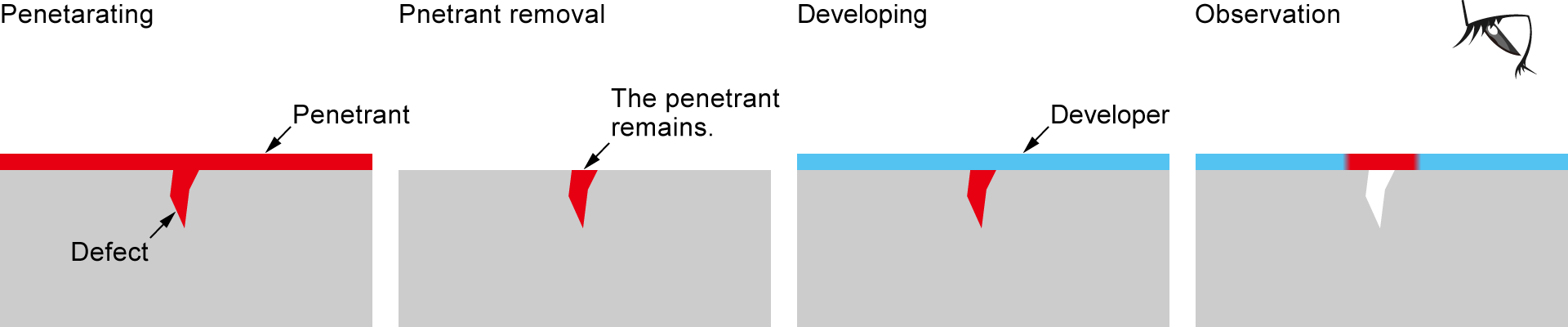
Penetrant Testing (PT)
Penetrant Testing (PT) refers to the process using the capillary phenomenon where a penetrant is used to coat an object and fill the inside of the defect.
After the process, the surface penetrant is removed.
The penetrant that has entered the defect cannot be washed out and remains, so by supplying a developer, the defect is absorbed and becomes visible. The PT is suitable only for surface defect inspection. It needs longer processes and greater time to complete, unsuitable for internal inspection.
It is used to inspect turbine blades of jet engines and automobile parts.
Other methods
The Hammering testing system has been conventionally handled by operators performing hammering and checking the internal condition by sound. It utilizes the same principle that an intact teacup produces a clear sound when struck, but a cracked teacup produces a muddy sound. The testing method is also used for checking bolt looseness, inspection of railroad axles and exterior building walls.
Visual checking is one of the easiest and simplest methods of Non-destructive testing. The visual appearance of objects is checked by staff.
The non-destructive testing helps improve the safety and security of industrial plants by offering advantages in quality control of castings, forgings, rolled products, pipes, welding processes, etc. It also provides better living reliability by maintaining transportation infrastructure such as bridges, tunnels, railroad wheels and axles, aircraft, ships, vehicles, etc., and inspecting daily life infrastructure such as turbines, pipelines, and tanks in power plants.
Moreover, NDT techniques will become more significant for advances in non-industrial situations such as surveys of cultural assets, art objects, fruit sorting, and thermographic testing.
Qualifications for Non-Destructive Testing (Japan)
In Japan, the Japanese Society for Non-Destructive Inspection (JSNDI) plays a central role in promoting NDT technology. In cooperation with the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) and related organizations, JSNDI conducts personnel qualification and certification to maintain high technical standards. Similar certification bodies, such as ASNT (American Society for Nondestructive Testing) or ISO-based certifications, exist globally to ensure the reliability of inspection personnel.
Reference (Japanese site)
- 日本非破壊検査協会 - 非破壊検査とは
(https://www.jsndi.jp/aboutus/aboutus02.html) - 日本非破壊検査協会 - 非破壊試験技術者制度
(https://www.jsndi.jp/qualification/) - DAKOTA JAPAN - 超音波探傷器の測定原理
(https://www.dakotajapan.com/product/u_f_detectors/principle/) - ジェムスエンジニアリング株式会社 - 非破壊検査試験・資格について
(https://www.jmsltd.co.jp/media/airticle/a48) - 神鋼検査サービス株式会社
(https://www.sisco.kobelco.com/licence/index.html) - minsaku
https://minsaku.com/category01/post247/ - OKIエンジニアリング - 超音波探傷検査(SAT)
(https://www.oeg.co.jp/analysis/sat.html) - OKIエンジニアリング - マイクロフォーカスX線CT・透過X線解析
(https://www.oeg.co.jp/analysis/fluoroscopy.html) - 非破壊検査株式会社 - 磁粉探傷試験
(https://www.hihakaikensa.co.jp/showcase/magnetic.html) - 非破壊検査株式会社 - 渦流探傷試験
(https://www.hihakaikensa.co.jp/showcase/eddy.html)
Related Technical Articles
- FAQs: Is a license required for usage of the X-ray inspection system?
- How to Choose an X-ray Inspection System
- What is the difference between radioactivity, radiation, and radioactive materials?
- Principles of Radiography
- Basics and Principles of Computed Tomography (CT)
- Understanding Radiation: Effects on the Body and X-ray Safety
- How to use X-ray Inspection System safely
Recommended products
Matsusada Precision offers a range of high-performance solutions ideally suited for non-destructive testing, including integrated X-ray modules, low-ripple high-voltage power supplies, and high-resolution X-ray inspection systems.







