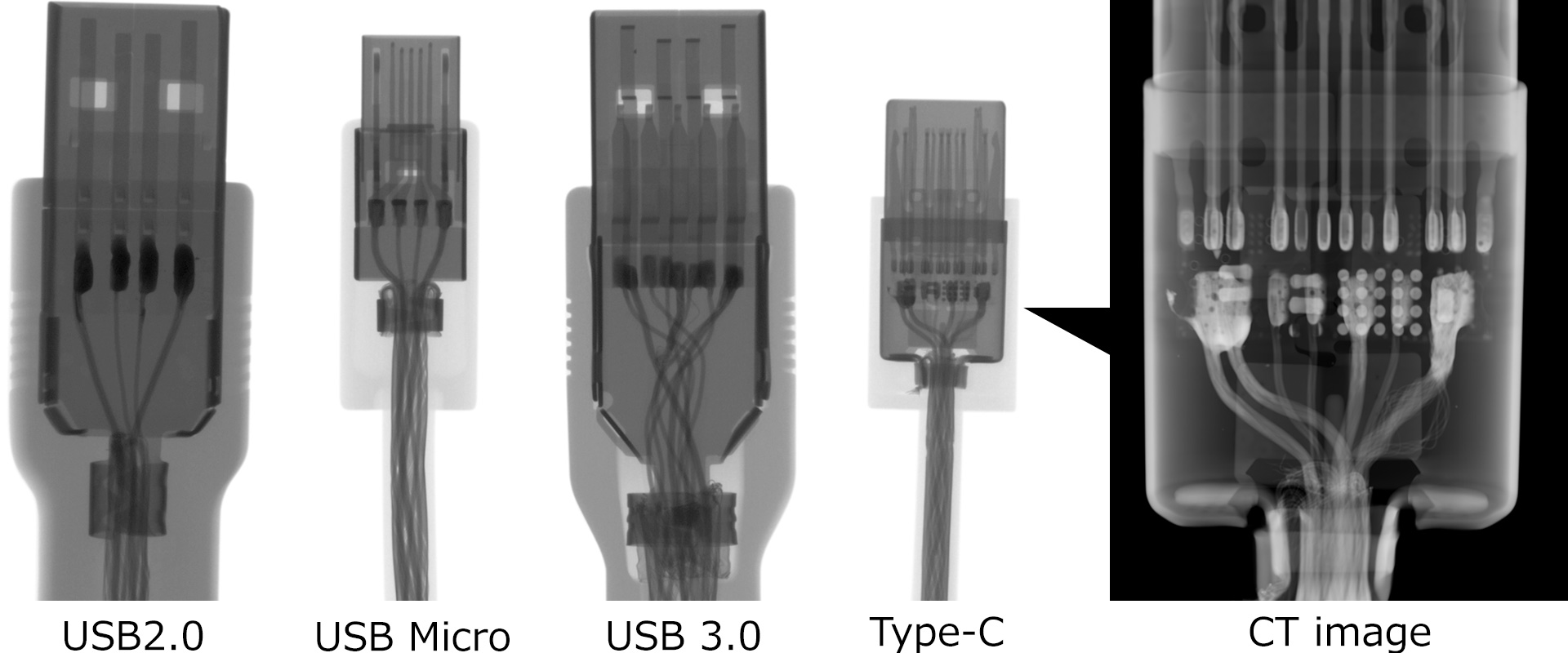
The X-ray images compare four different USB cables (from left to right): USB 2.0, USB Micro, USB 3.0, and Type-C cables. These represent the standard USB connector configurations: Type-A, Micro-B, Type-A, and Type-C, respectively. The X-ray examination reveals their internal structures, showing that USB 2.0 and Micro USB have four buses each, while USB 3.0 and Type-C feature six buses. The size comparison shows that Type-A has the largest, followed by Type-C, then Micro-B. A distinctive feature of the Type-C connector is the presence of an internal circuit board, which is clearly visible in the X-ray image.
X-ray system requirements
| Focal spot | Microfocus |
|---|---|
| X-ray tube voltage | 130 kV |
Recommended products
Related Technical Articles
- Selecting an X-ray Inspection System
- Principles of Radiography
- Safe Operation of X-ray Inspection Systems
- What is Microfocus X-ray Technology? (Basic Knowledge)
- Basics and Principles of Computed Tomography (CT)
- Non-Destructive Testing: Types and Applications
- What are X-rays? (Basic Knowledge)
- How to Acquire High-Quality Computed Tomography (CT) Images - X-ray NDT series (1)
- A Guide to X-ray CT Images: Formats, Viewing, and Applications - X-ray NDT series (2)
- X-ray Image Processing and Automated Inspection - X-ray NDT series (3)
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies
- What is the difference between Radioactivity, Radiation, and Radioactive Materials?
- Understanding Radiation: Effects on the Body and X-ray Safety





