The following X-ray images compare the internal structures of four different batteries. Arranged from left to right, the samples include an AA manganese battery, an AA alkaline battery, an AA nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) battery, and an 18650 lithium-ion battery.




| Battery Types | Structural Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Manganese battery | The key structural difference between manganese and alkaline batteries is visible in the arrangement of the active materials. In the X-ray image, the zinc and manganese components show varying contrast levels due to the difference in atomic number, with the denser zinc appearing darker. |
| Alkaline battery | |
| Nickel-metal hydride battery | This battery features a distinct internal structure with an insulating separator. Due to the high density of the nickel composition, the negative electrode appears significantly darker in the X-ray image compared to other materials at the same exposure level. |
| Lithium-ion battery | The internal structure consists of cathode and anode sheets wound together with separators in a spiral configuration (jelly roll), all contained within a cylindrical metal case. |
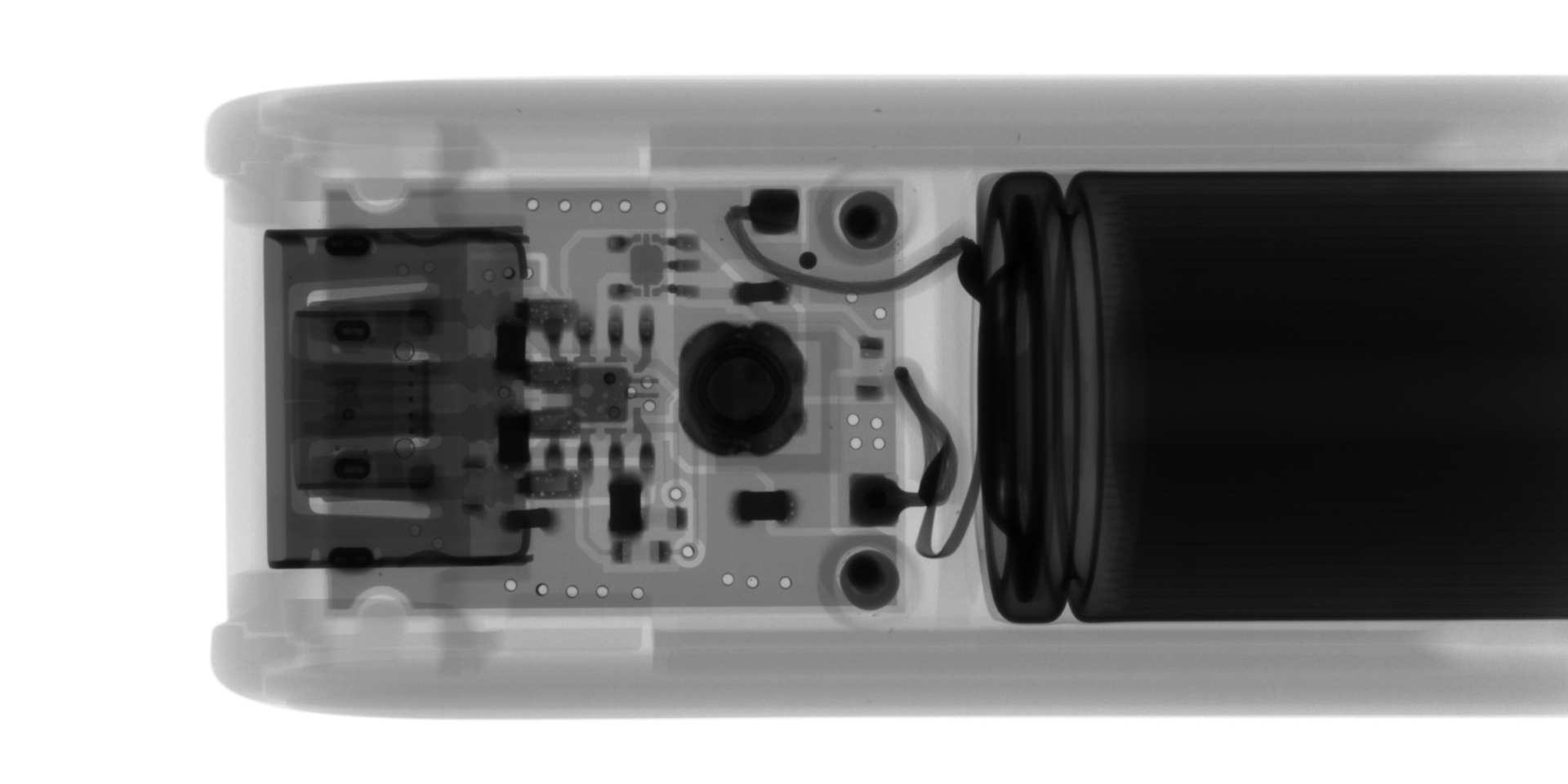
Internal Inspection of a Mobile Battery Charger
The X-ray image of a mobile battery charger reveals the placement of internal components, including the USB terminal, circuit board, and connectors. The high-resolution scan clearly visualizes the soldering conditions, through-holes, and internal trace patterns on the PCB, facilitating non-destructive failure analysis.
X-ray System Requirements
| Focal Spot | Microfocus |
|---|---|
| X-ray Tube Voltage | 130 kV |
Recommended products
Related Technical Articles
- Selecting an X-ray Inspection System
- Principles of Radiography
- Safe Operation of X-ray Inspection Systems
- What is Microfocus X-ray Technology? (Basic Knowledge)
- Basics and Principles of Computed Tomography (CT)
- Non-Destructive Testing: Types and Applications
- What are X-rays? (Basic Knowledge)
- How to Acquire High-Quality Computed Tomography (CT) Images - X-ray NDT series (1)
- A Guide to X-ray CT Images: Formats, Viewing, and Applications - X-ray NDT series (2)
- X-ray Image Processing and Automated Inspection - X-ray NDT series (3)
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies
- What is the difference between Radioactivity, Radiation, and Radioactive Materials?
- Understanding Radiation: Effects on the Body and X-ray Safety






