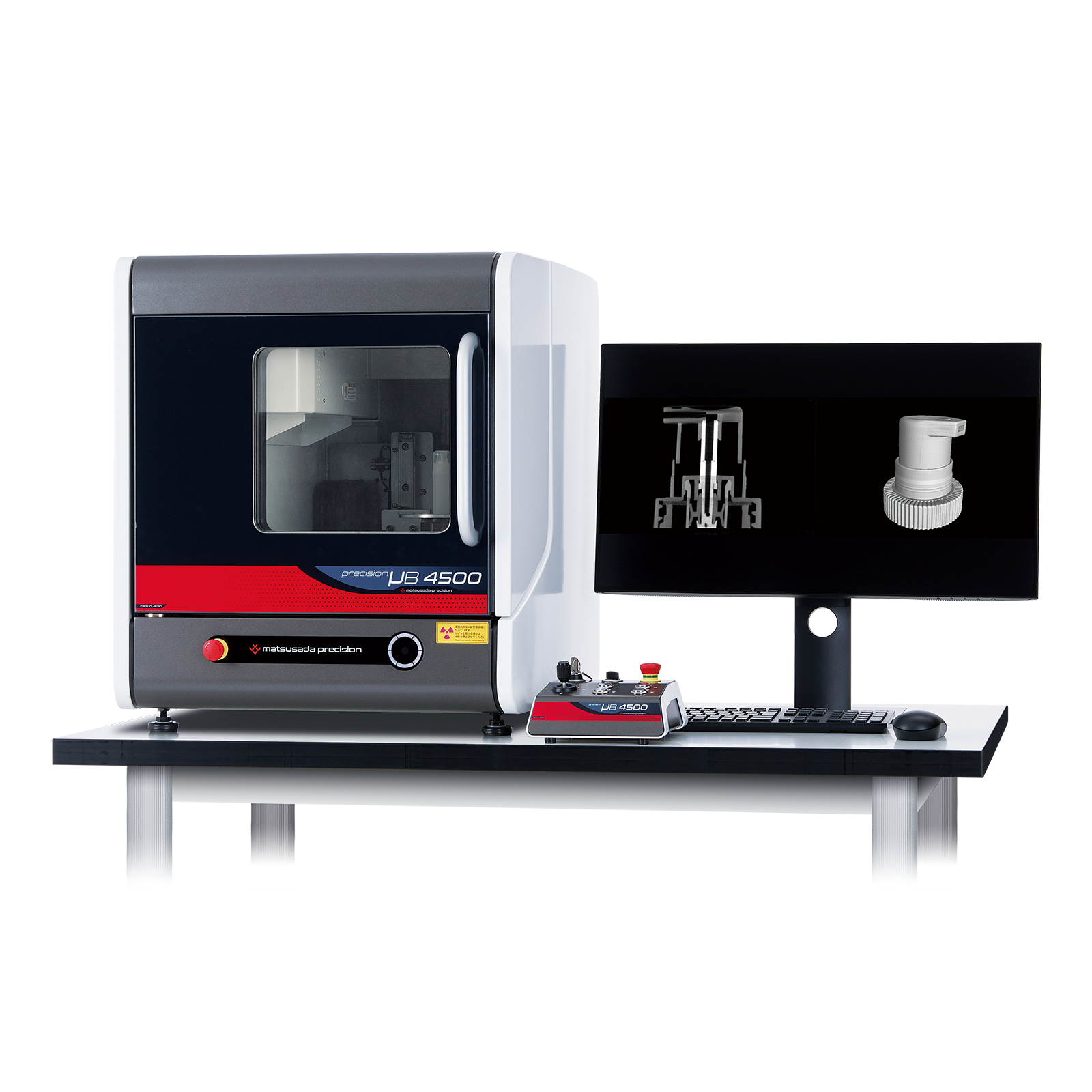
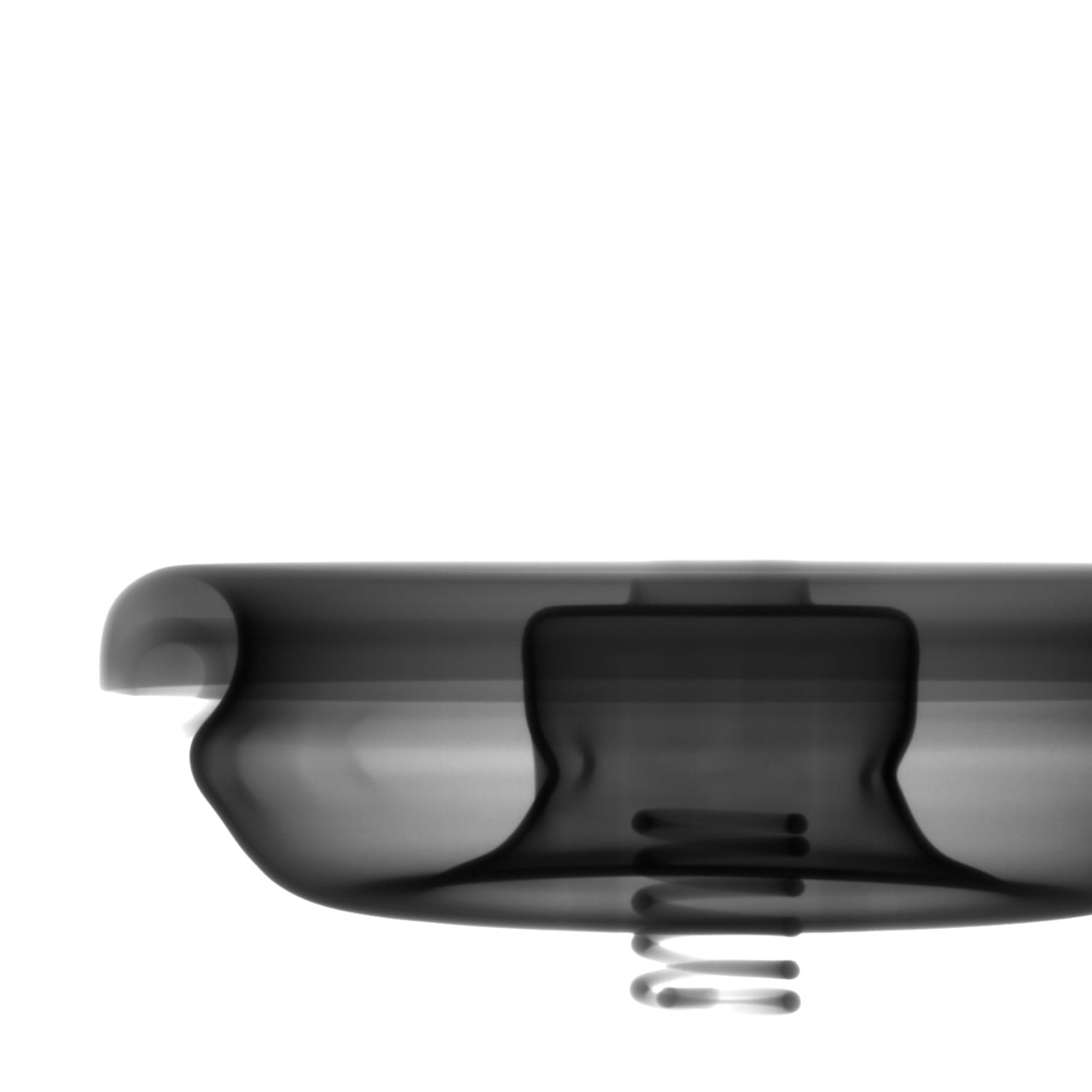
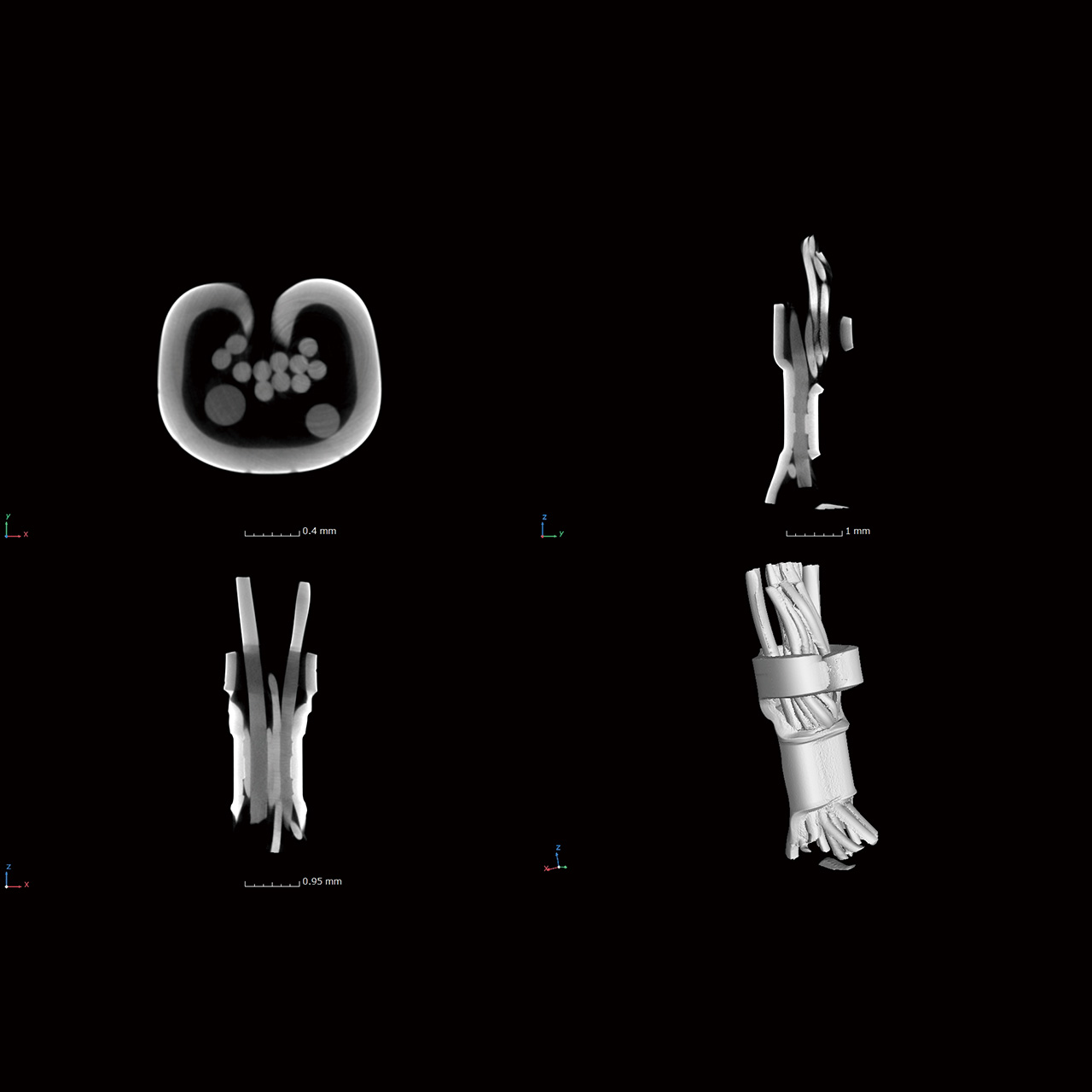
The precision µB4500 is a compact benchtop micro-CT scanner. Despite its small footprint, it delivers high-resolution 3D-CT imaging and high magnification comparable to larger systems. It allows for non-destructive inspection of internal structures for a wide range of samples, including material composites and biological specimens.
The precision μB4500 is a high-performance benchtop micro-CT scanner. Despite its compact, lab-friendly footprint, it delivers exceptionally high-resolution and high-magnification 3D-CT data, rivaling that of larger systems.
This scanner is designed to provide outstanding micro-CT imaging for a wide range of samples. It is an ideal tool for researchers and engineers in materials science, life sciences, and advanced manufacturing who require non-destructive, sub-micron level visualization of internal structures. The μB4500 reveals intricate details in material composites, biological specimens, and complex micro-devices, offering unprecedented insights for R&D and quality assurance.

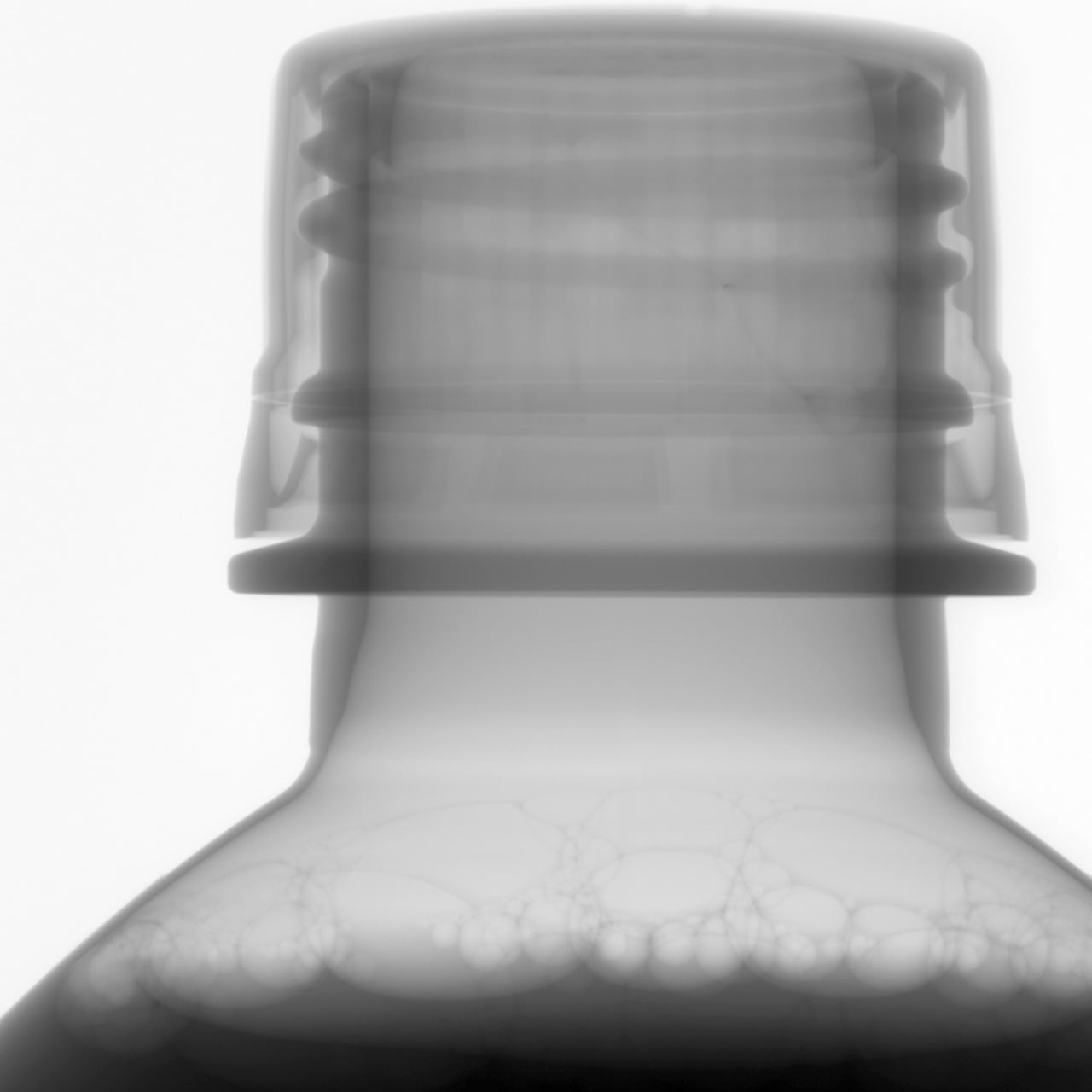
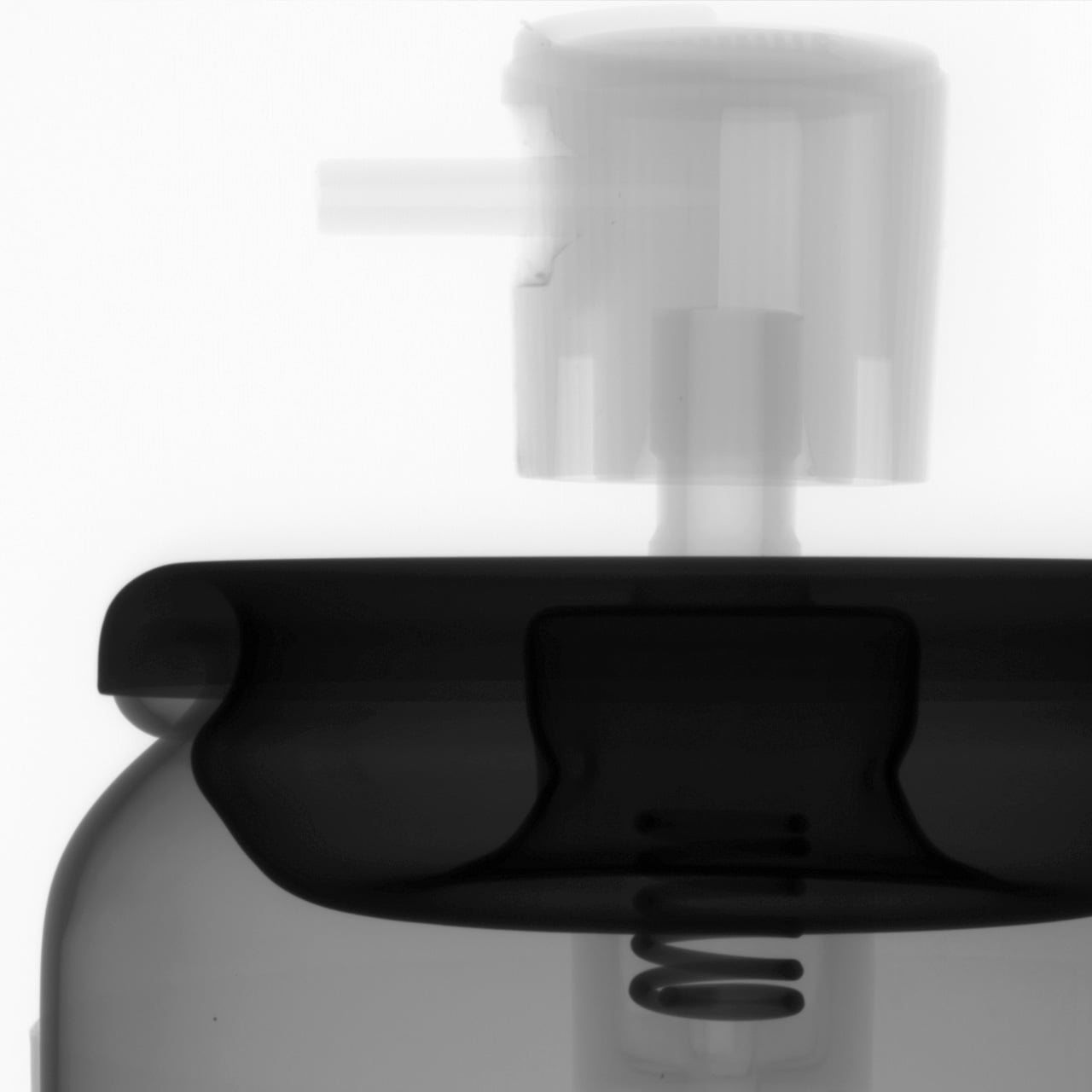
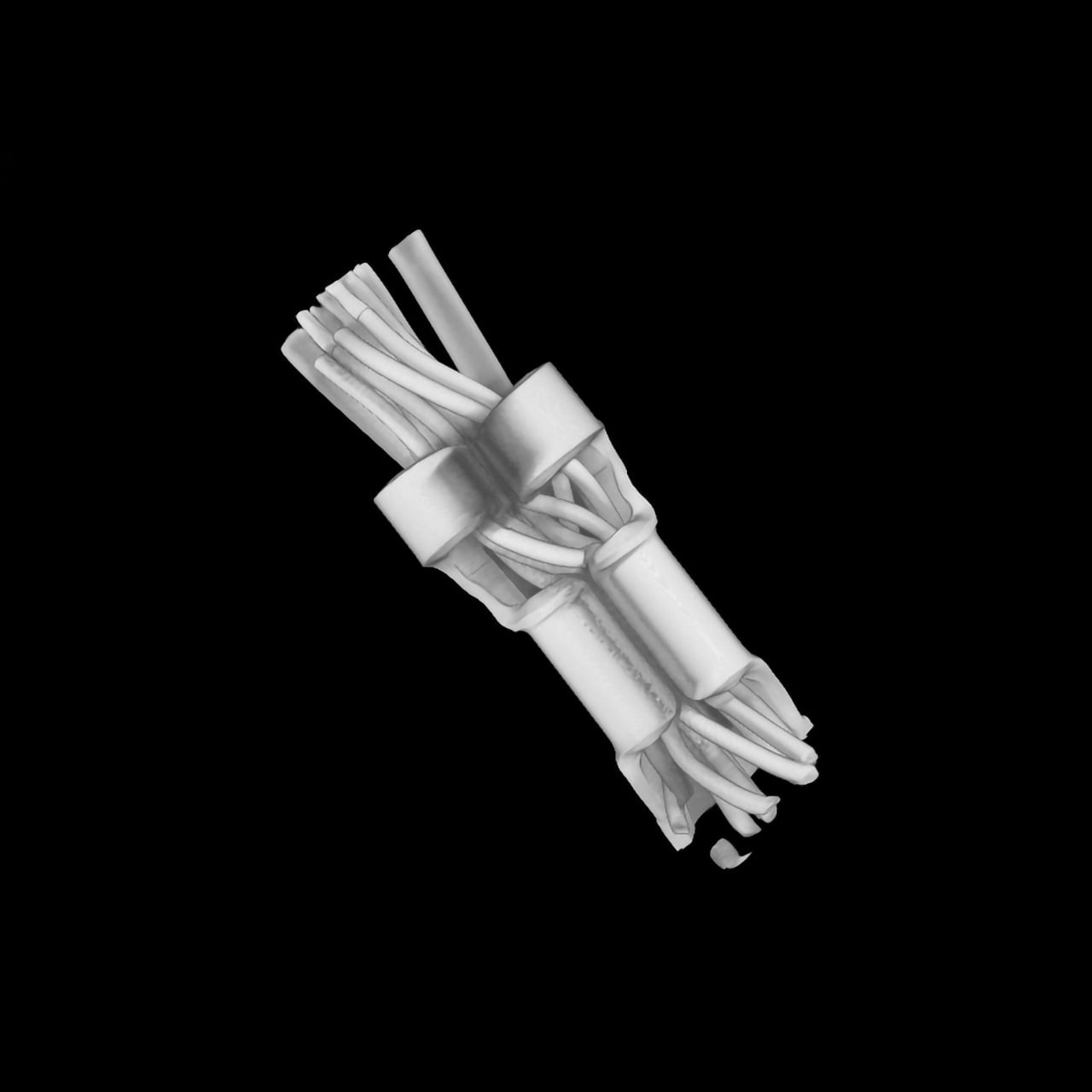
Ideal for imaging liquids and powders
The horizontal beam configuration allows samples to sit naturally on the rotating stage. This design ensures stability for fluid or loose powder samples during scanning, eliminating the need for complex fixing mechanisms or tilting that could disturb the specimen.
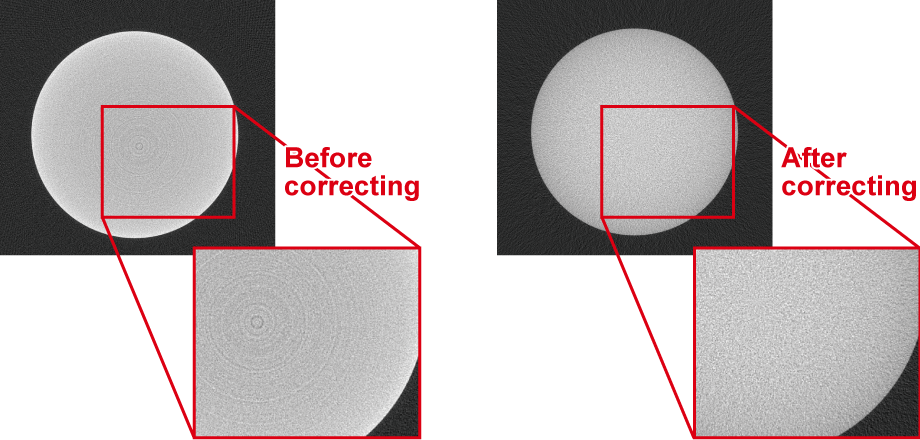
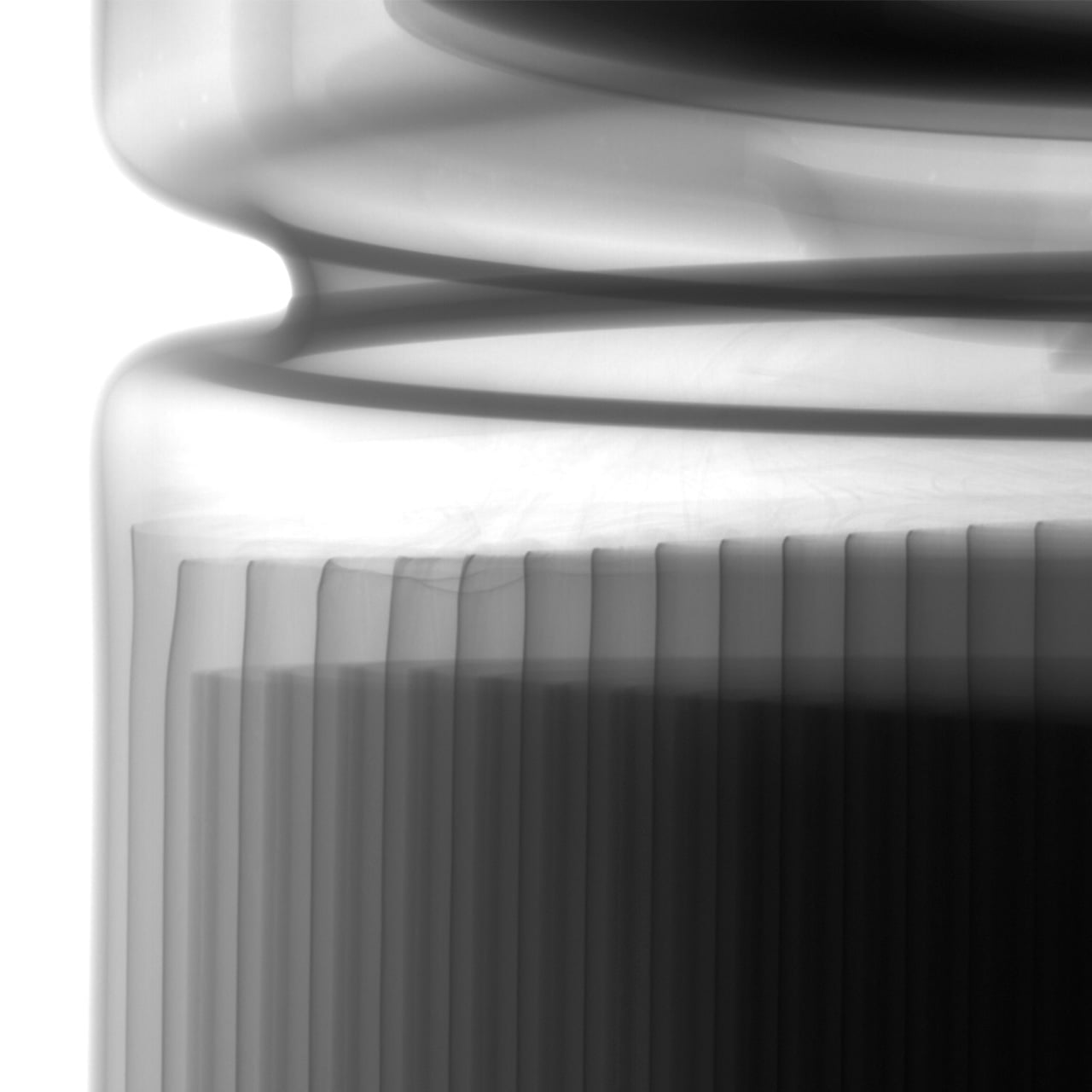
High-quality tomography with artifact reduction
The precision µB4500 utilizes dedicated software with advanced artifact reduction algorithms. This allows for clear imaging of mixed-material samples with varying densities, such as resin and metal composites, which are typically difficult to inspect due to metal artifacts.
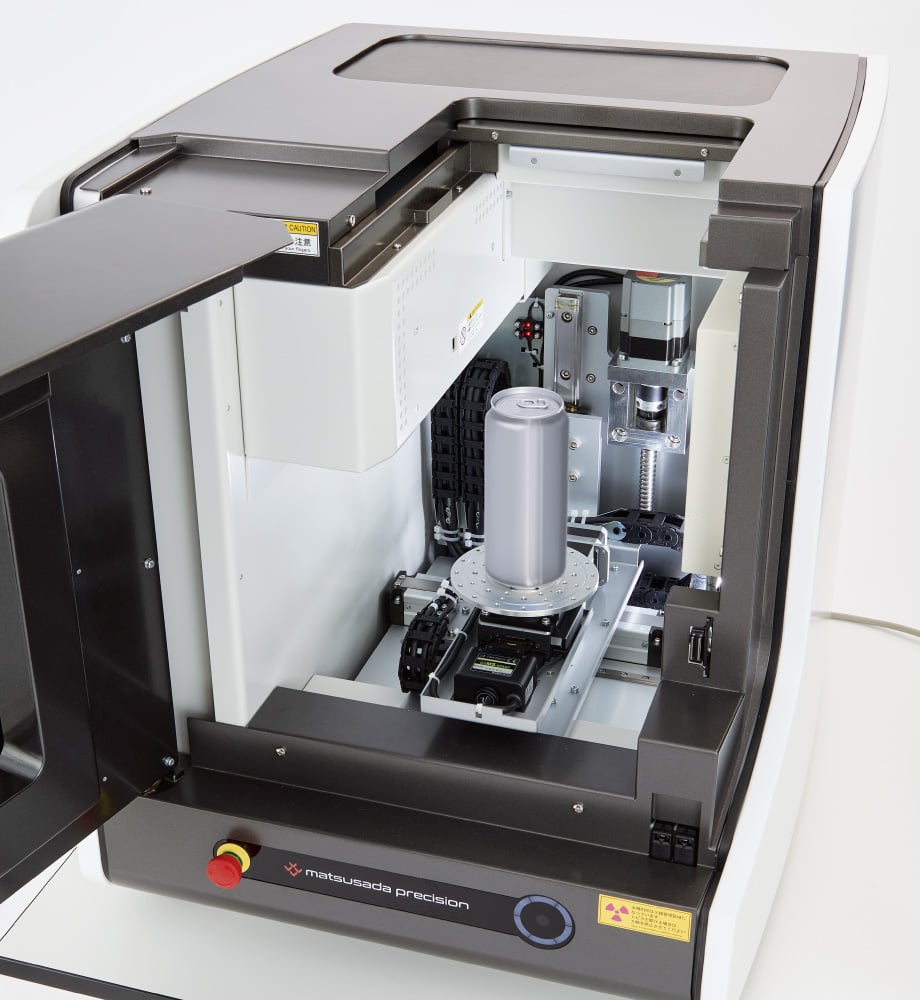
Tall sample inspection in a compact body
Tall samples can be taken in and out smoothly using a sliding door on the top.
With the dimensions 570 mm wide, 665 mm deep, and 625 mm high, the precision µB4500 offers a compact solution even for tall sample inspection. Regardless of the sample shape or location, you can install the X-ray inspection benchtop anywhere in small offices, space-constrained factories, and laboratories.
Dimensions W: 570 x D: 665 x H: 625 mm
Stage Ø: 120 mm
Available sample size Ø: 120 x H: 175 mm

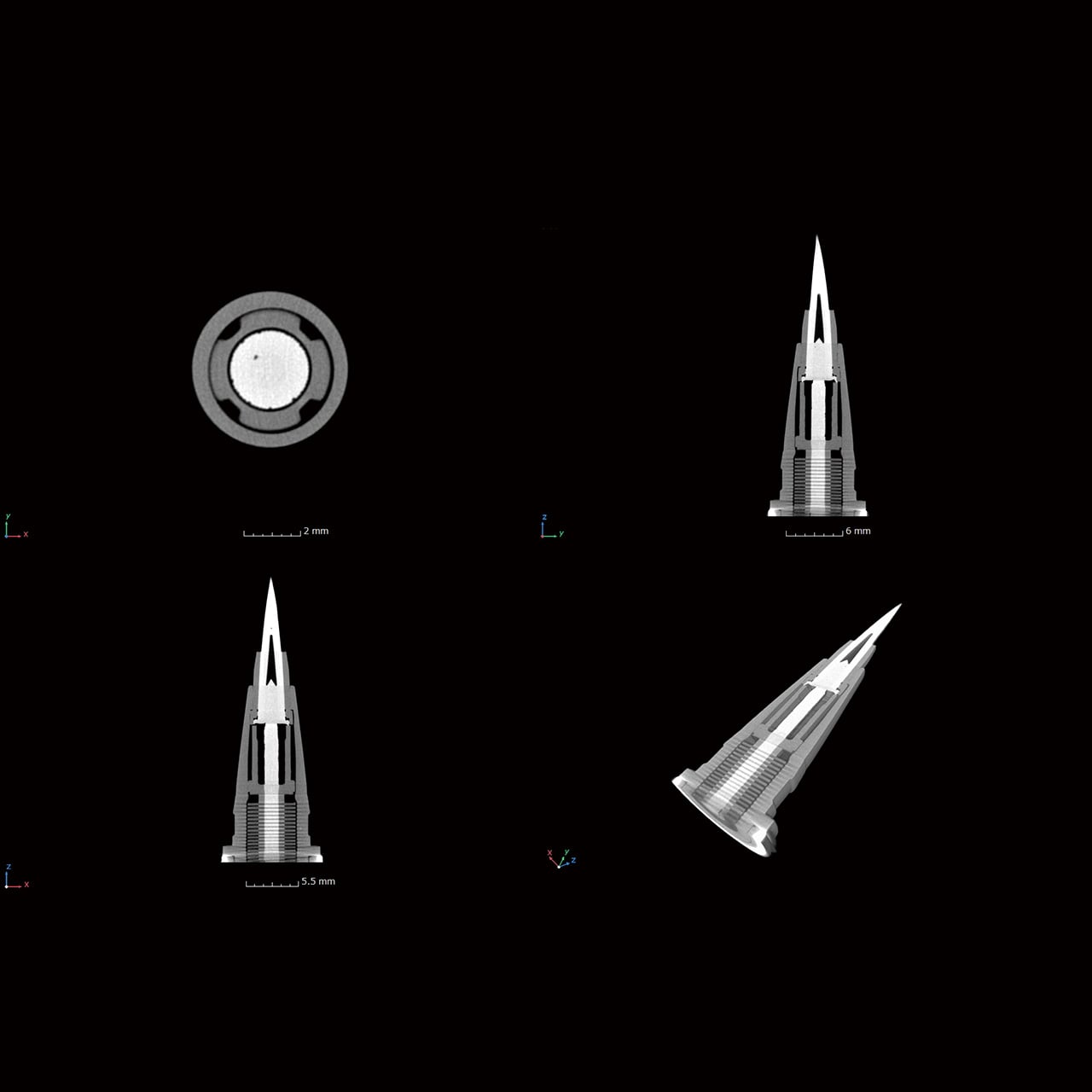
High-resolution X-ray camera for wide field of view
3-mega pixel camera as standard: optional 6-mega pixel camera
With the industry's highest level of resolution, a 3-megapixel flat panel detector (FPD) (*6-megapixel with option), the precision µB4500 offers high magnification for a wide observation area. A large sample image can be shot in one field.
Datasheets
If you are unable to download a file
Please try the following solution.
- Please press Ctrl+F5 to clear the cache of your web browser and try again.
- Please restart your web browser and log in again to try again.
- Please change your web browser to another browser and try again.
- Restart the computer and try again.
- Please try again on a different computer.
Login Required
-

precision µB4500
Date: 2025-08-07 rev 07
PDF (7,216 KB) -

Microfocus X-Ray Inspection System Selection Guide
Date: 2025-05-07 rev.06
PDF (13,911 KB) -

Micro View X-Ray CT System Guide
Date: 2025-09-12 Rev 08
PDF (4,989 KB)
Related Technical Articles
Similar products
-

precision µB3600
- X-ray Tube Voltage
- 90 kV
- X-ray Power
- 13.5 W
X-ray Inspection SystemBenchtop High-spec Model
-
New

precision µB3200
- X-ray Tube Voltage
- 60 kV
- X-ray Power
- 9 W
X-ray Inspection SystemBenchtop Entry Model
-

precision μX7800
- X-ray tube voltage
- 90 kV
- X-ray power
- 18 W
X-ray Inspection SystemVersatile General-Purpose Model
Product Lineup:
X-ray Inspection SystemsUser Support
FAQ
- What is Micro‑focus X‑ray?
- What is the tube voltage for X‑ray inspection systems?
- Is a license required for usage of X‑ray inspection system?
- How should the optimal X‑ray tube voltage be determined?
- What is the difference between medical and industrial CT scans?
- What is the difference between an X‑ray inspection system and a CT scan system?