A flat panel detector (FPD) is a digital X-ray imaging device widely used in radiography. Much like a digital camera sensor converts visible light into images, an FPD converts X-ray energy passing through an object into digital signals to generate high-resolution radiographic images.
FPDs are essential components in X-ray CT, medical radiography, and mammography systems. They have largely replaced conventional image intensifiers (I.I.) and imaging plates (IP) because they offer a wider dynamic range and enable real-time imaging without separate reading processes.
Types of X-ray FPDs
There are two primary methods for converting X-rays into electrical signals:
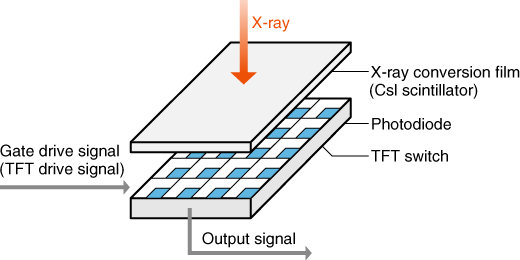
- Indirect Conversion: This method uses a scintillator to convert X-rays into visible light, which is then detected by a photodiode array. Typically, this method does not require high-voltage bias for the detector element.
- Direct Conversion: This method uses a semiconductor material, such as amorphous selenium (a-Se) or cadmium telluride (CdTe). A high-voltage bias is applied across the semiconductor layer. When X-rays strike the material, they generate electrical charges that are guided by the high-voltage field to a Thin-Film Transistor (TFT) array for readout.
Power Supplies for FPD Applications
Matsusada Precision offers compact, low-noise high-voltage power supplies designed to provide the stable bias voltage required for direct conversion FPDs (a-Se and CdTe). Our power supplies help ensure clear, artifact-free imaging by minimizing power supply noise.
- Related Terms:
-
- Direct Conversion
- Flat Panel Detector (FPD)
- amorphous Selenium (a-Se)
- direct X-ray conversion
- Imaging Plates (IP)
- X-ray image intensifier (I.I.)
- Radiography
- Computed Tomography (CT)
- X-ray image sensor
Recommended products
We offer power supplies for applying the high voltage required by selenium films.
Related Technical Articles
- Principles of Radiography
- Safe Operation of X-ray Inspection Systems
- How to Acquire High-Quality Computed Tomography (CT) Images - X-ray NDT series (1)
- A Guide to X-ray CT Images: Formats, Viewing, and Applications - X-ray NDT series (2)
- X-ray Image Processing and Automated Inspection - X-ray NDT series (3)
- What is the difference between Radioactivity, Radiation, and Radioactive Materials?
- Understanding Radiation: Effects on the Body and X-ray Safety
- Non-Destructive Testing: Types and Applications
- What are X-rays? (Basic Knowledge)
- What is Microfocus X-ray Technology? (Basic Knowledge)
- Basics and Principles of Computed Tomography (CT)









