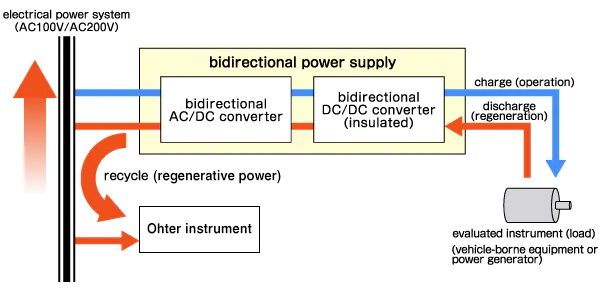
Bidirectional power supplies, also known as regenerative power supplies, provide both source and sink capabilities in a single unit. This is essential for applications such as battery charge/discharge cycle testing, which typically requires a power source for charging and an electronic load for discharging.
Unlike conventional setups that require physically switching connections between separate instruments, a bidirectional power supply transitions seamlessly between sourcing and sinking. During sink operation (discharging), the absorbed energy is efficiently returned to the AC grid (regenerated) rather than being wasted as heat. This significantly reduces overall energy consumption.
Additionally, these units function as high-performance battery simulators. This makes them an ideal choice for evaluating automotive components, such as on-board chargers (OBCs) and power inverter circuits.
Related articles
- What is Regenerative Energy and how it works?
- How to Use Bidirectional Power Supply
- What is a power inverter? (Basic knowledge) How does it work, and what is it used for?
- Electric grid (power system interconnection) to Learn from Scratch
- Electric Vehicle Motors: Power Supply and Battery Voltage
- Battery Types and Characteristics of Charge Control
- What is an Electronic Loads? (Basic Knowledge)
- Application: Photovoltaics (PV)
- Application: Inverter (Power inverter)




