Photovoltaic (PV) is the generation of electricity using solar cells that convert sunlight energy into electrical energy. PV is also referred to as solar cells, modules, panels, or arrays, depending on the scale. Solar power is generated by using solar panels, which are made up of solar cells laid out in series or parallel.
Photovoltaic power can be generated on a small scale. The solar panels are attached to road signs and street lights in combination with batteries as a source of electricity for nighttime lighting. Photovoltaic power is also attracting attention as renewable energy. For example, eco-friendly houses combining solar panels and storage batteries are on the rise. In recent years, increasing mega-solar power plants have been built by installing many solar panels on vacant sites.
Photovoltaic Power Generation System generally consists of a "solar cell panel," "charge/discharge controller," "storage battery," "solar inverter," and "load."
The systems can be broadly classified into "Stand-alone (off-the-grid) PV systems" and "Grid-connected PV systems," and they have the following characteristics.
- Off-the-grid PV System
-
It can be divided into systems for DC loads and AC loads.
Fig.1 shows the stand-alone PV system where all the circuits, including the loads, consist of DC.Fig.1: DC stand-alone PV system 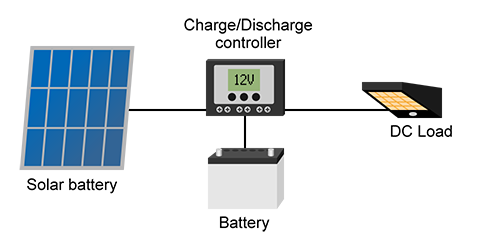
-
When using a load that operates on AC power, such as home appliances, the solar inverter is used to convert the DC power generated by the solar cells into AC power, as shown in Fig.2 below.
As a disadvantage, however, it cannot be used as the battery runs out of remaining capacity. Also, inverters consume power constantly. Even when there is no load, You should note the inverter's standby power.Fig.2: AC stand-alone PV system 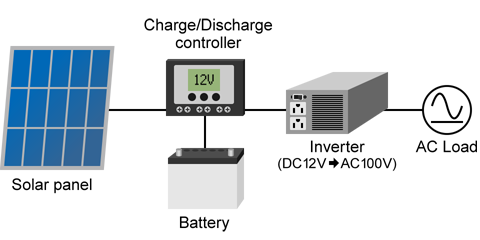
- Grid-connected PV system
-
The grid-connected PV system is a system where the power system is connected to a power company's grid. You can sell the generated power to the power company.
Fig.3: Grid-connected PV system for residential use 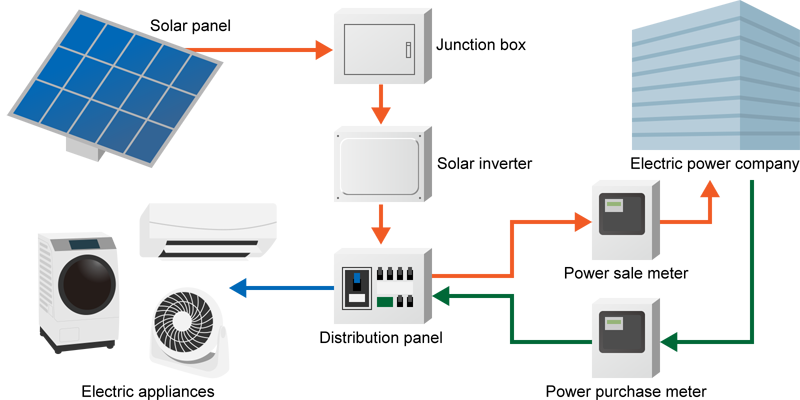
-
Here is an example of a PV system using household batteries to store electricity.
You can purchase the electricity shortfall. It is called a Home Energy Management System (HEMS) or Partial off-grid solar in Japan.Fig.4: PV / Battery system for residential use 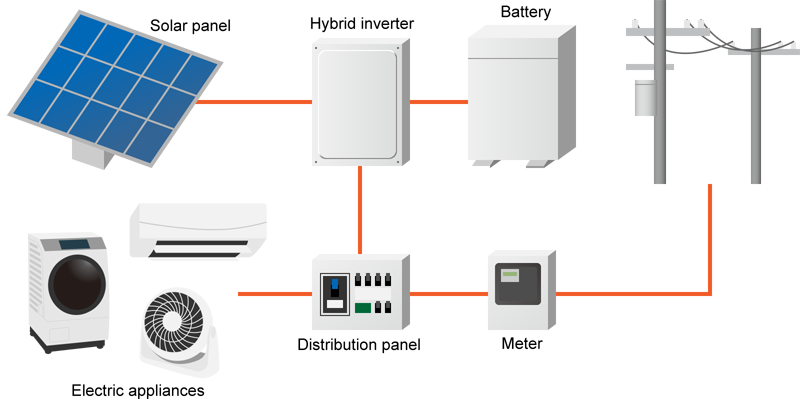
The electricity produced by solar panels is direct current (DC). It needs to be converted to alternating current (AC) to be used in homes and factories. So we use solar inverters to convert the DC power to AC, as shown in the figure below.
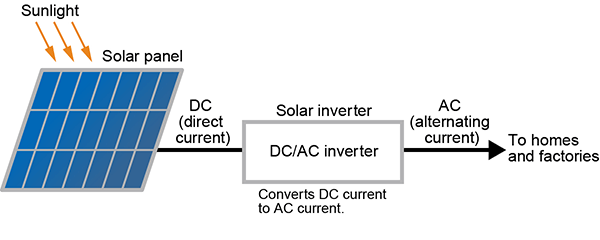
Developing solar inverters for PV, requires a DC power supply of about 300 to 600 V instead of solar cells. In such development and testing, a DC power supply called a solar array simulator or PV simulator is installed on the input side, and an AC electronic load is on the output side.
Matsusada Precision offers a broad range of high-voltage power supplies and regenerative power supplies (bidirectional power supplies) suited for developing and manufacturing solar inverters and batteries.
Abbreviations for photovoltaic:
MPPT: Maximum Power Point Tracking
PWM: Pulse Width Modulation
STH: solar-to-hydrogen efficiency
- Related words:
-
- Solar Cell
- Perovskite solar cell (PSC)
- Solar Power
- Inverters
- Battery
- Energy Storage
- Solar Panel
- Mega Solar
- Solar/Photovoltaic
- Solar cell manufacturing equipment
- HEMS
- Partial off-grid solar
Recommended products
High-voltage power supplies and regenerative power supplies (bi-directional power supplies) for the development and manufacturing of solar inverters and batteries















