Mechanism of Bidirectional Power Supply
A bidirectional power supply is a device capable of managing a two-way flow of electrical energy, featuring internal converters for both AC/DC and DC/DC conversion. This design enables the unit to handle both power sourcing and sinking (regeneration).
A key feature of a bidirectional power supply is its regenerative capability, which allows it to return energy to the grid rather than dissipating it as heat. For this reason, the terms "bidirectional power supply" and "regenerative power supply" are often used interchangeably in this context.
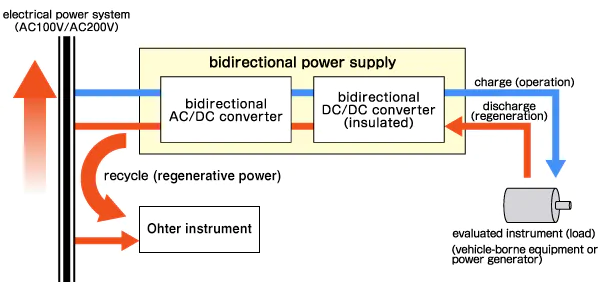
The figure below illustrates the schematic of a typical bidirectional power supply.
This architecture enables bidirectional energy exchange with the commercial power grid. The circuit connected to the Device Under Test (DUT) acts as the regenerative power supply.
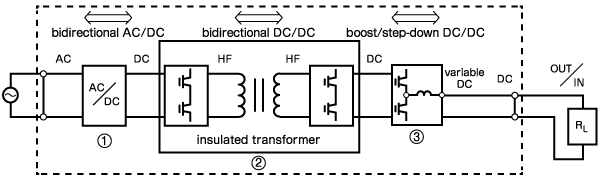
The internal circuitry generally consists of three stages:
Bidirectional AC/DC Converter: This circuit converts AC grid power to DC and vice versa, enabling energy exchange with the power line.
Bidirectional DC/DC Converter (Isolation Transformer): This stage provides galvanic isolation between the primary (grid) side and the secondary (output) side while regulating DC power flow.
Boost/Step-down DC/DC Converter: This final stage adjusts the voltage to meet specific testing requirements, allowing for variable voltage output to the DUT.
Advantages of Using Bidirectional Power Supply
Bidirectional power supplies function as advanced battery simulators. With the proliferation of portable electronic devices and EVs, testing how devices respond to battery voltage fluctuations is critical. Batteries exhibit complex behaviors: voltage drops as output current increases, and electrical characteristics shift depending on whether the battery is fresh, fully charged, or degraded.
A standard DC power supply cannot easily simulate these dynamic conditions. However, a programmable bidirectional power supply can emulate various battery states, serving as an ideal tool for development and testing.
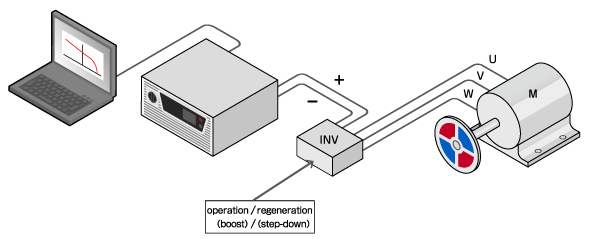
For high-power applications, such as EV converter testing, bidirectional power supplies handle the necessary high voltages and currents. A major advantage is the ability to perform seamless transitions between powering (sourcing) and regeneration (sinking). This prevents voltage notches at the crossover point and eliminates current waveform overshoot or undershoot. This capability ensures stable testing conditions without the risk of overcharging or damaging actual rechargeable batteries.
Use Case 1: As a Constant Voltage/Constant Current (CV/CC) Power Supply
Use as a Constant Voltage/Constant Current power supply
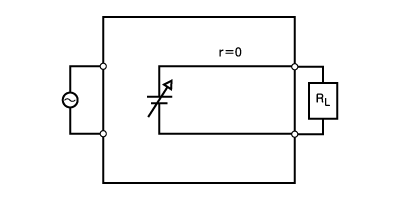
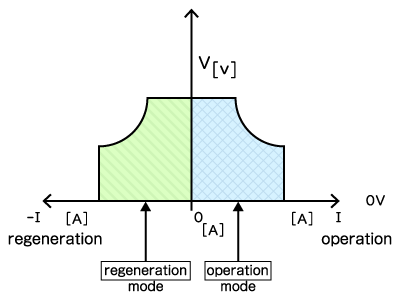
To verify system reliability, it is essential to test how a device withstands voltage fluctuations. Using a power supply to emulate these changes is often more efficient and repeatable than using actual batteries.
While a standard power supply can simulate a primary battery (constant source), a bidirectional power supply is required to simulate rechargeable batteries effectively. It can reproduce the voltage characteristics of various chemistries, such as lithium-ion or lead-acid batteries, ranging from 12 V automotive batteries to high-voltage EV packs.
Use Case 2: Simulating Internal Resistance and Battery Degradation
The internal resistance of the rechargeable battery can be set to reproduce the operation of the battery
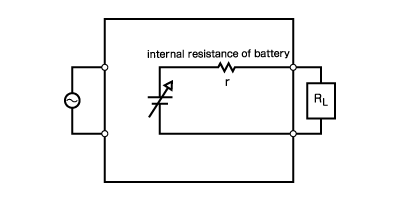
By adjusting the value 'r', it is possible to simulate how the internal resistance changes with the state of charge (SOC) and other parameters (SOD etc.)
Battery voltage can be changed by Constant Voltage setting when using as a CV power supply in the case r=0 (Ω)
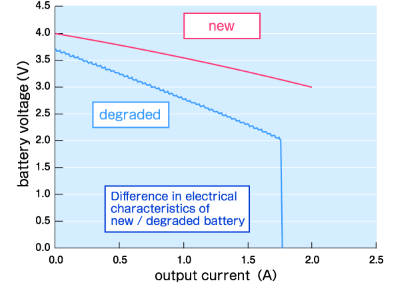
Real-world batteries experience degradation over time. This includes permanent degradation (aging) and temporary performance reduction (e.g., due to low temperatures). A battery's State of Charge (SOC) and State of Health (SOH) significantly impact its output characteristics.
By utilizing the variable internal resistance function of a bidirectional power supply, engineers can simulate a battery's State of Degradation (SOD). This allows for the testing of electronic devices under "aged battery" conditions--ensuring that products function correctly or trigger appropriate low-battery warnings even when the power source is not ideal. This prevents malfunctions and ensures reliability across the product's entire lifecycle.
Measurement example for V-I characteristics of lithium-ion battery (case of discharging)
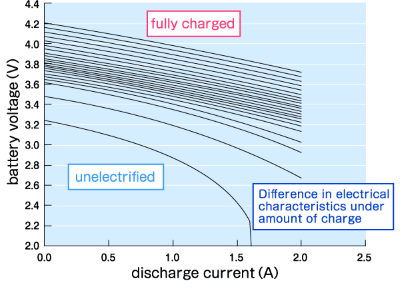
V-I characteristics
Use Case 3: Automotive and Hybrid System Simulation
Beyond consumer electronics, bidirectional power supplies are essential for automotive testing, particularly for hybrid and electric vehicles. For instance, "48 V Mild Hybrid" systems utilize regenerative braking and motor assistance, requiring robust power management between 48 V and 12 V systems.
Since standard automotive electronics operate at 12 V, a DC/DC converter bridges the gap to the 48 V generator. A bidirectional power supply serves as a simulator for these generators and converters, verifying that the energy management system functions correctly under dynamic driving conditions.
Related Technical Articles
Recommended products
Matsusada Precision manufactures DC power supplies with regenerative functions, inverters, and power supply equipment used to evaluate batteries.
Reference (Japanese site)
- Japanese source page 「双方向電源の使われ方」
(https://www.matsusada.co.jp/column/column-bi-directional-power-supply.html) - 双方向 DC/DC コンバータの各種回路方式
(https://hirachi.cocolog-nifty.com/kh/files/29160601-1.pdf) - 双方向DC-DCコンバータと蓄電システムの協調によるスマートなパワーシステム
(https://product.tdk.com/ja/techlibrary/applicationnote/power-system_bidirect-converter.html) - 電気が伝わる経路(電気事業連合会)
(https://www.fepc.or.jp/enterprise/souden/keiro/) - 48Vマイルドハイブリッドシステムとは?仕組みや燃費への効果も全て解説!
(https://carblo.net/48v-mild-hybrid-system) - 「バッテリマネジメント工学」足立修一・廣田幸嗣編著 東京電機大学出版局刊
(https://www.tdupress.jp/book/b348995.html) - 「電気自動車工学」廣田幸嗣・小笠原悟司編著 森北出版株式会社刊
(https://www.morikita.co.jp/books/mid/074311)






