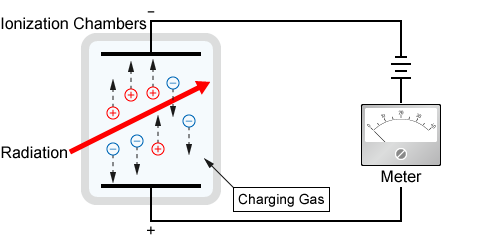
An ionization chamber is a type of radiation detection device. In an ionization chamber, two opposing electrodes are placed in a container filled with gas, and a high voltage is applied. As the charged particles (radiation) pass through the gas, the gas molecules are ionized to produce ions and electrons.
The applied electric field causes these electrons to drift toward the positive electrode (anode) and the positive ions toward the negative electrode (cathode). This movement of charges constitutes an electric current, which is measured to detect and quantify the radiation. If the voltage applied to the electrodes is too low, the separated ions and electrons will recombine before they reach the electrodes. Therefore, a sufficient voltage of several tens to several hundred V is required in the ionization chamber.
A proportional counter is one in which the voltage in the ionization chamber is increased above a certain level. When the voltage is increased, the strong electric field between the electrodes accelerates the electrons created by the incident radiation.
The accelerated electrons secondarily ionize the gas molecules, resulting in a current that is larger than the primary ionization current. Proportional counters make use of this amplification effect. GM (Geiger-Müller) tubes are another type of gas-filled radiation detector. They operate at an even higher voltage, where a single ionization event triggers a cascading avalanche of secondary ionizations throughout the gas.
Matsusada Precision offers a wide range of high-voltage power supplies ideal for ionization chambers, featuring low ripple, a compact design, and ratings up to 1 kV and beyond.
- Related Terms:
-
- Accelerator
- Radiation
- Radiation detection
- Proportional counter
- GM tube
- Ionization
Recommended products
There are a large number of high-voltage power supplies that can be used for ionization chambers, featuring low ripple, a compact body, and ratings of 0 to 1 kV.
Related Technical Articles
- What are X-rays? (Basic Knowledge)
- Safe Operation of X-ray Inspection Systems
- What is the difference between Radioactivity, Radiation, and Radioactive Materials?
- Understanding Radiation: Effects on the Body and X-ray Safety
- Safety and Usage of High Voltage Power Supply
- How to Handle Electric Shock and High Voltage
- High Voltage Measurement Method