An ion beam is a beam produced by accelerating ions at high speed. Ion is an atom or mass of atoms that are positively or negatively charged. Ion acceleration is to move an ion to the destination by applying an arbitrary voltage. The kinetic energy gained by the ions is proportional to the accelerating voltage. Depending on the application, various electrodes are used to manipulate the ion beam, including accelerating, extraction, suppression, and deflecting electrodes. They are used in ion engines, ion beam sputtering, ion implantation, focused ion beam (FIB), and accelerators. To prevent charge buildup on non-conductive samples, which can deflect the ion beam, the sample surface is often electrically neutralized. This is typically achieved using a flood of low-energy electrons from a device called a "neutralizer."
To generate an ion beam for FIB, a liquid metal ion source (LMIS) consisting of a needle-shaped tungsten filament with gallium attached is used. When a strong electric field is applied to the liquid metal tip via an extraction electrode, an ion beam is emitted from the tip through field evaporation. A heater is used to keep the metal in a liquid state. The generated ions are then controlled by the accelerator's electric and magnetic fields to form a narrow, directional stream. Ion beam steering is used in ion beam scanning. Ions that are extracted from the ion source are focused by a condenser lens (CL), and the ion beam is scanned by an electrostatic deflector. Ion beams are used for a wide range of applications such as ion beam implantation, ion beam processing, and scanning ion microscope (SIM).
The ion beam generator consists of an ion source (ion gun), an electromagnetic lens in the accelerator, and a deflector. The ion beam passes through an accelerator and is used for ion implantation of impurities into semiconductors, surface cleaning by ion milling, surface processing, surface modification, and surface and internal analysis. The ion beam is accelerated and decelerated by an electric field in a vacuum and deflected by a magnetic field. Ion mass sorting is performed by bending the ions in a magnetic field, and energy analysis is performed using techniques such as retarding field analysis or electrostatic deflection analysis.
Matsusada Precision offers a variety of power supply equipment for ion acceleration, extraction, suppression, deflection, focusing, gridding and neutralization. Matsusada Precision power supplies designed for electrostatic deflectors have various kinds of specifications, and especially we provide high voltage amplifiers featuring the world's highest level of response speed. The integrated DC bias function allows for easy adjustment of the scanning reference point.
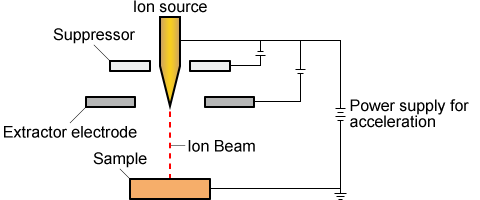
- Ion source conceptual diagram
-
- Related Terms:
-
- ion beam
- ion source
- ion gun
- acceleration
- ion acceleration
- accelerator
- ion implantation
- impurity implantation
- beam transport deflection
- surface processing
- surface modification
- electrostatic deflection (including ion beam steering)
- ion milling
- electrostatically controlling ion beams
- electrostatic lenses
Recommended products
Matsusada Precision offers integrated ion beam power supplies that combine all necessary outputs for ion extraction, acceleration, deflection, focusing, and grids. We also provide individual power supply devices for each of these specific applications.


















