Flat panel displays (FPDs) are ubiquitous in modern electronics, utilized in smartphones, automotive dashboards, medical instruments, and large-screen televisions. Key technologies in this sector include Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs), Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs), and Quantum Dot LEDs (QLEDs).
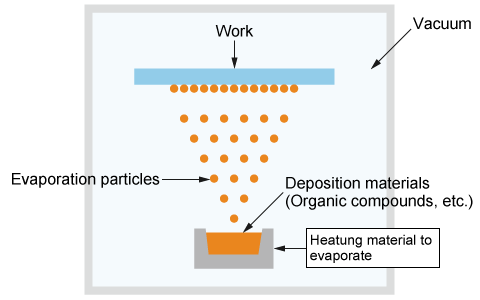
The manufacturing of these displays requires high-precision processes, such as Thin-Film Transistor (TFT) array fabrication and rigorous lighting inspection. In OLED production specifically, organic layers are often formed on substrates using vacuum vapor deposition. This process typically employs resistive heating to evaporate materials, requiring strict temperature control to ensure uniform film thickness.
Matsusada Precision offers high-performance programmable DC power supplies optimized for these demanding environments. Our power supplies provide the stable, precise output control essential for resistance heating deposition sources and other critical FPD manufacturing applications.
- Related Terms:
-
- LCD
- OLED
- QLED
- OLED display
- Film formation
- Resistance heating deposition
- Heater control
Recommended products
Matsusada Precision's programmable DC power supplies are widely used in FPD manufacturing equipment for these demanding applications.







