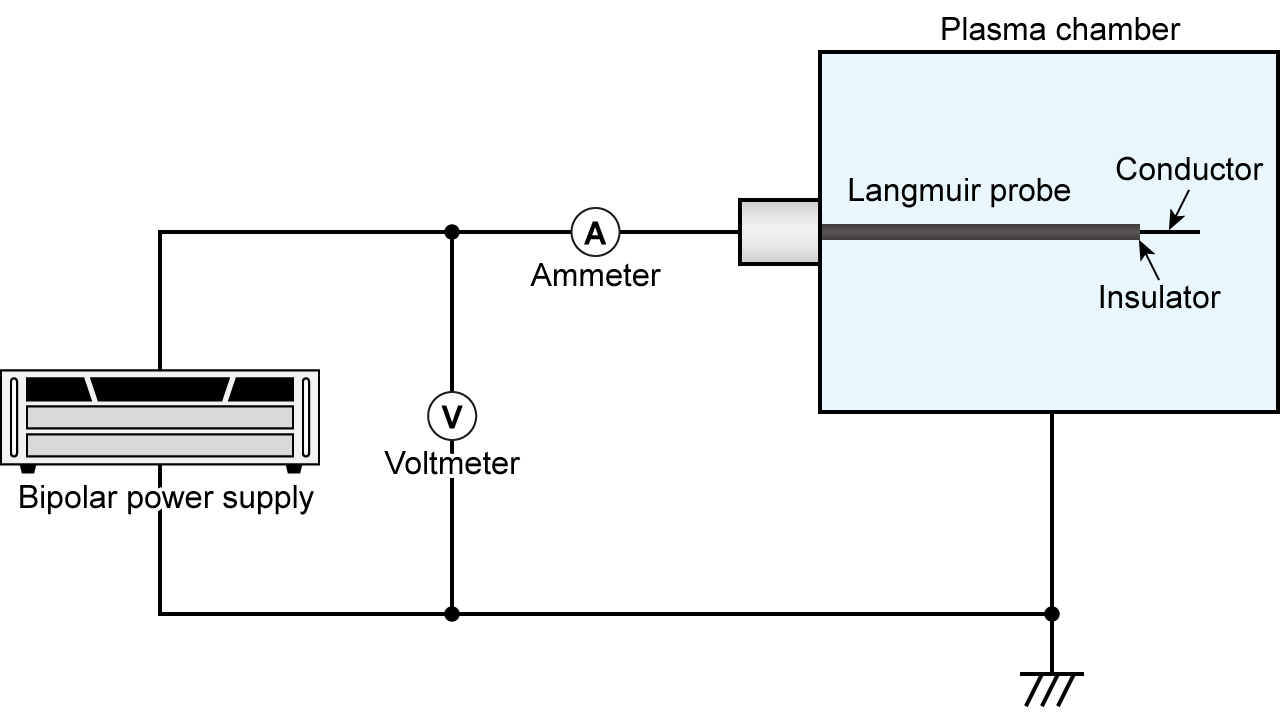
The Langmuir probe is a diagnostic tool used to measure key plasma parameters, such as electron density, electron temperature, and plasma potential, in various plasma systems, including tokamak fusion reactors.
In the Langmuir probe method, a four-quadrant bipolar power supply is used to apply a swept voltage (typically a triangular or sine wave) to a probe immersed in the plasma. The resulting current-voltage (I-V) characteristic is then analyzed to determine the plasma's properties.
The specifications of the bipolar power supply required for plasma measurements depend on the electron temperature, electron density, and plasma potential.
A typical setup uses a four-quadrant power supply with a voltage range of ±100 V, a current capacity of 1-2 A, and a bandwidth sufficient for sweep frequencies of around 100 Hz. Some applications, however, may require high-voltage amplifiers capable of delivering up to ±4000 V, such as our AMJ series.
Langmuir probes are essential tools in tokamak fusion research and are also used to measure the electron energy distribution function (EEDF) inside the vacuum vessel.
- Related Terms:
-
- Plasma
- Vacuum Plasma Treatment
- Nuclear fusion
- Fusion power generation
- Tokamak
- Plasma actuator
- Biconic cusp
- EEDF
- vacuum vessel






