Bipolar power supplies (also known as four-quadrant power supplies) are capable of sourcing and sinking current at both positive and negative voltages. This allows them to handle complex loads and generate various waveforms--such as DC, sine waves, and arbitrary waveforms--at high speeds.
Selecting the Right Unit: Power Supply vs. Amplifier Matsusada Precision categorizes these products based on their signal source:
Bipolar Power Supply: A four-quadrant power supply with a built-in function generator for autonomous waveform generation.
Bipolar Amplifier: A high-speed unit designed to amplify external input signals. (High-voltage models are classified as High-Voltage Amplifiers).
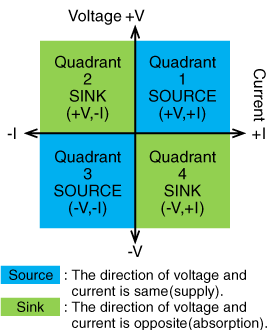
The four quadrants represent the relationship between voltage and current direction:
-
Quadrant I (+V, +I): Source operation (Positive Power Supply)
Outputs positive voltage and positive current. -
Quadrant II (+V, -I): Sink operation (Positive Electronic Load)
Absorbs current while maintaining positive voltage. -
Quadrant III (-V, -I): Source operation (Negative Power Supply)
Outputs negative voltage and negative current. -
Quadrant IV (-V, +I): Sink operation (Negative Electronic Load)
Absorbs current while maintaining negative voltage.













