What is Haptics?
Haptics is a technology that engages the sense of touch by providing tactile feedback, such as vibration or force, to the user. This technology simulates physical interactions on screens and interfaces, enabling more intuitive and realistic control. Common examples include smartphone vibration alerts and force feedback in gaming controllers.
Core Principles and Methods of Haptics
While there are several methods for generating tactile feedback, here we introduce three of the most prominent techniques.
1. Vibrotactile Feedback
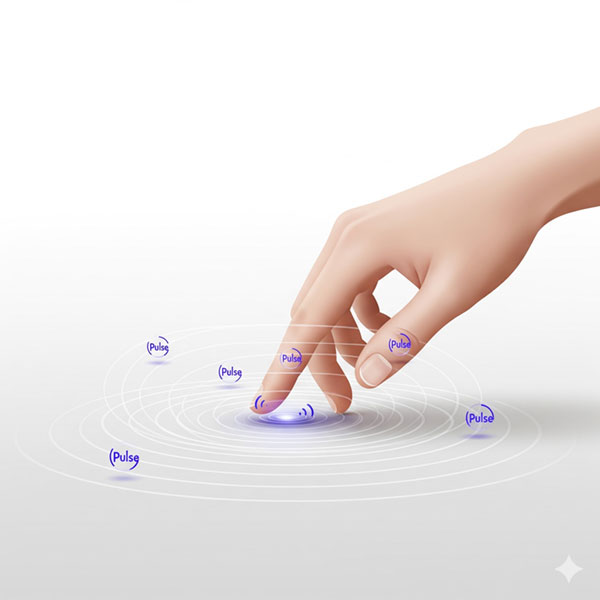

This is the most widely used method, employing actuators like motors or piezoelectric elements to transmit vibrations directly to the skin, thereby creating a sensation of touch. Its popularity stems from its simple structure, ease of miniaturization, and low-cost implementation.
2. Force Feedback/Kinesthetic Sensation
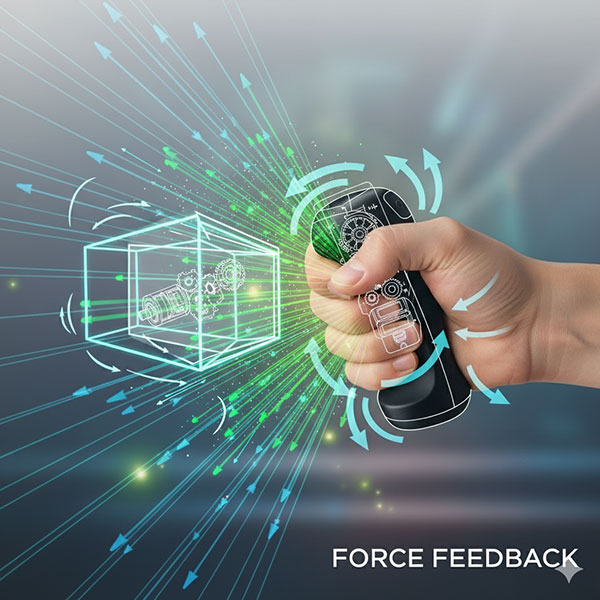

This method provides a sense of an object's weight, hardness, or resistance by applying a counter-force to the user's movements. It is utilized in applications such as surgical training simulators to create a highly realistic and immersive experience.
3. Electrostatic Haptics
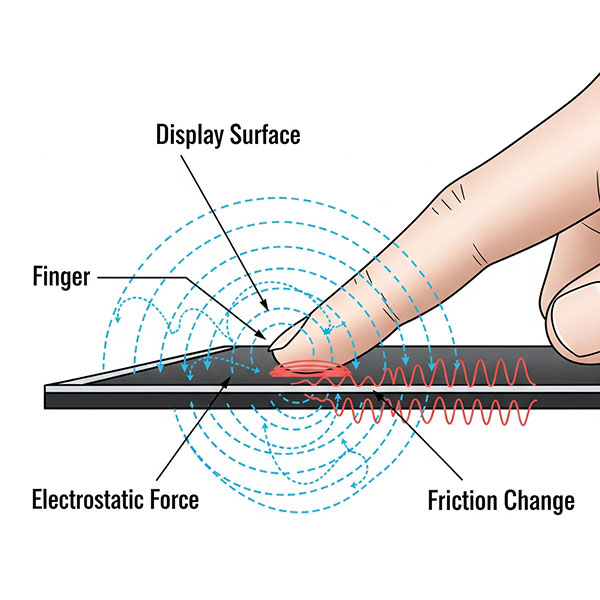
By generating a weak electrostatic field on a surface like a display, this technique modulates the frictional forces between the surface and the user's fingertip. This allows it to simulate a wide range of surface textures, such as roughness or smoothness.
Expanding Applications for Haptic Technology
Haptic technology holds great promise not only in the entertainment industry but also as a key technology for solving societal challenges.
Tactile Support for the Visually Impaired
Haptics can significantly improve information accessibility for individuals with visual impairments by converting visual information into tactile sensations.
- Tactile Displays: These devices render on-screen shapes, graphs, and maps three-dimensionally using an array of micro-pins or piezoelectric elements. Users can then recognize the information by touching the surface, allowing them to intuitively grasp visual data that was previously difficult to convey.
- Mobility Support and Navigation: By embedding vibrating elements into white canes or wearable devices, these systems can indicate the direction of travel or the location of obstacles through different vibration patterns and directions, supporting safer navigation.
Future Haptic Experiences (Expo 2025 Osaka, Kansai)
Haptic technology holds immense potential not only in the medical and welfare fields but also for the future of communication and entertainment. Expo 2025 Osaka, Kansai is a focal point for experiencing this cutting-edge technology. At the "Future Healthcare" showcase, Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. plans to demonstrate the advanced 3D haptic technology of its group company, MIRAISENS, Inc.
This technology uses a special device that, when touched, generates specific vibrations and patterns of skin deformation. This realistically recreates the feeling of pressure, texture, and resistance of an object, making it feel as if it were actually there. Visitors will be able to touch virtual objects directly and feel their texture, providing an unprecedented and highly immersive experience.
Matsusada Precision's Technology: Powering Advanced Research
Achieving high-definition and responsive haptics--particularly for high-resolution tactile displays--requires driving piezoelectric elements with exceptional speed and precision. Controlling numerous piezoelectric elements individually demands amplifiers capable of high-fidelity waveform output. Leveraging decades of expertise in high-voltage and precision power supply technology, Matsusada Precision provides robust support for haptics research and development.
Piezoelectric Actuators
Matsusada Precision's PZA and PZ series piezo actuators are widely adopted in haptics R&D at leading institutions, supporting studies on vibration propagation and tactile sensitivity.
-
Nagoya Institute of Technology:
"
Possibility of Tactile Sensitivity Change by Manipulation of Skin Vibration Propagation
"
Piezo Actuator Used: PZA12-6 -
Tohoku University:
"
Dependence of the Perceptual Discrimination of High-Frequency Vibrations on the Envelope and Intensity of Waveforms
"
Piezo Actuator Used: PZ12-112
Piezo Drivers (High-Voltage Amplifiers)
Our piezo drivers deliver the wide bandwidth and high slew rate essential for high-speed piezo operation. They ensure faithful reproduction of complex vibration waveforms.
DC Power Supplies
Reliable, low-noise power ensures system stability. Our DC power supplies, such as the R4K-80, perform exceptionally in demanding motor-driven applications and force sensation displays.
-
The University of Electro-Communications:
"
Vibrotactile and Pseudo-Force Sensation Display Using Motor Rotational Acceleration
"
DC Power Supply Used: R4K-80
At Matsusada Precision, we continue to deliver compact, high-performance products built on the foundation of Japanese quality and reliability.
If you are developing haptic devices or any application using piezoelectric elements and require precision high voltage power supply, high voltage amplifier, or DC power supply, please do not hesitate to contact us. We can propose the optimal solution tailored to your specifications and also accommodate custom requests. Let Matsusada Precision be your partner in accelerating your research and development.
- Related Terms:
-
Fundamentals/General Terms
- Haptics
- Tactile Feedback
- Haptic Device
- Haptic Interface
- Haptic Technology
- Haptic Display
-
Technical Methods
- Vibrotactile Feedback
- Force Feedback
- Kinesthetic Feedback
- Electrostatic Haptics
- Friction-based Haptics
-
Application Fields
- Smartphone Vibration
- Game Controller Haptics
- VR Haptic Device
- AR Haptic Device
- Wearable Haptics
- Medical Simulator Haptics
- Haptics for Visually Impaired
- Navigation Haptics
-
Components/Hardware
- Piezo Actuator
- Piezoelectric Actuator
- Piezo Driver
- High Voltage Amplifier
- High Voltage Power Supply
- DC Power Supply
- Bipolar Power Supply









