A floating power supply is one whose output is electrically isolated from its input and the chassis ground. Unlike standard DC power supplies, where one output terminal is typically connected to earth ground, a floating power supply allows its entire output to be "floated" or referenced to an external voltage potential. This is possible because a floating power supply is designed with high dielectric strength (high isolation) between its input and output circuits.
The main applications of floating power supplies are power supplies for microchannel plates used in detectors of mass spectrometry, power supplies for filaments of anode-grounded X-ray tubes, power supplies for filaments, grids, bias, and electrostatic lenses of scanning electron microscopes (SEM), and transmission electron microscopes (TEM), and power supplies for filaments, suppressor electrodes (suppressors), extractor electrodes (extractors), and condenser lenses of focused ion beam (FIB) devices.
When selecting a floating power supply, it is crucial to ensure that the external voltage to which the supply will be floated does not exceed the unit's specified isolation voltage (dielectric strength). The supply must also meet the voltage and current requirements of the load.
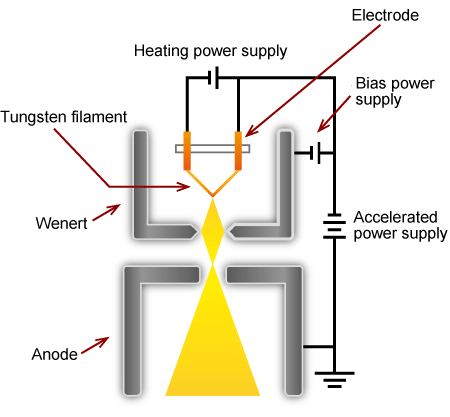
In this diagram, both the filament heating power supply and the Wehnelt bias power supply are floating power supplies, referenced to the high-voltage potential of the electron gun.
Matsusada Precision offers the FDCS, MDC, and FDC series as highly isolated low-voltage DC power supplies for floating high-voltage power supplies. We also provide the XPg series X-ray tube power supplies, the SEM series scanning electron microscope power supplies, the HEB series electron beam power supplies, and the HIB series ion beam power supplies, which all integrate floating power supplies into a system.










