Dielectric breakdown testing is a destructive procedure used to determine the breakdown voltage of an insulating material. By applying a gradually increasing voltage, engineers can identify the precise point at which the material fails and becomes electrically conductive.
While often discussed alongside similar tests, it is important to distinguish between the following terms:
- Dielectric Breakdown Test: A destructive test designed to measure the absolute breakdown voltage limit where insulation fails.
- Withstand Voltage Test: A pass/fail test used to verify that a material or component can endure a specific voltage level for a set time without failure.
- "Hi-Pot" (High Potential) Test: A common industry term generally referring to electrical safety testing, often used synonymously with withstand voltage testing.
Insulators are fundamental to these tests. They are substances such as glass, resin, and rubber that inhibit electrical conduction. Materials specifically engineered to possess high insulation resistance and superior dielectric strength are classified as insulating materials.
Insulating materials are utilized to block the flow of electricity to unintended areas. Common examples include the plastic casing of electrical outlets and the insulation on electrical wires. In systems utilizing high-voltage power supplies, ensuring the reliability of these insulators is paramount. An insulation failure (electrical leakage) can lead to severe accidents, including electric shock, fire, or significant equipment damage. The dielectric breakdown test is a fundamental procedure conducted to verify this critical reliability.
The dielectric breakdown test is standardized by international and regional bodies, including IEC 60243-1, ASTM D149, and JIS C2110, which define the test conditions. The test determines the maximum voltage an insulating material can withstand before failure (breakdown).
The Dielectric Breakdown Testing Method
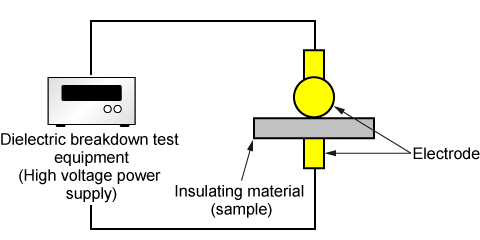
The testing method involves applying a precisely controlled, gradually increasing high voltage to the material or component under test (DUT). The voltage is continuously ramped up from zero until the material fails and dielectric breakdown occurs.
During this process, the test equipment, which is centered around a stable high-voltage power supply or amplifier, continuously monitors the leakage current. When the insulation fails, a sudden, large increase in current (an electrical arc) occurs. The power supply must immediately detect this event, shut down its output to ensure safety, and precisely record the voltage at which the failure occurred. This value is the material's breakdown voltage.
Matsusada Precision offers an extensive lineup of high-performance high-voltage power supplies designed for the rigorous demands of dielectric breakdown testing. Reflecting our commitment to "Made in Japan" quality, our products deliver the exceptional stability, low noise, and precise control required by development engineers and researchers. With maximum outputs up to 200 kV, our compact, reliable, and sophisticated power supplies provide the ideal solution for evaluating a wide variety of materials.
Dielectric breakdown test equipment
- Related Terms:
-
- Insulating Materials
- Withstand Voltage
- High Voltage Insulation Resistance
- Dielectric Strength
- IEC 60243-1
- ASTM D149
- JIS C2110
- JIS K6911
- Insulation breakdown test
- Dielectric withstand test
- Hipot testing











