A bipolar power supply is a unit capable of outputting both positive and negative voltages. Matsusada Precision defines this category as power supplies featuring a built-in signal source (function generator) and full four-quadrant operation.
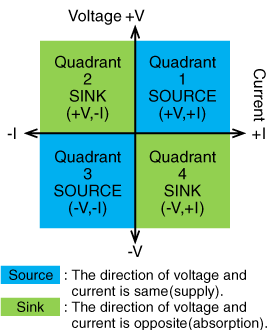
The four operating quadrants are defined as follows:
First quadrant: Voltage (+) and Current (+) – Supplying power (Source mode)
Second quadrant: Voltage (+) and Current (-) – Absorbing power (Sink mode)
Third quadrant: Voltage (-) and Current (-) – Supplying power (Source mode)
Fourth quadrant: Voltage (-) and Current (+) – Absorbing power (Sink mode)
Because they operate across all four areas, these units are also known as "four-quadrant power supplies." They can function not only as DC power sources but also as electronic loads.
While generally classified as DC power supplies, bipolar power supplies offer wider bandwidth and higher speed operation. The integrated function generator allows the output of alternating current (AC) and automotive cranking waveforms without external equipment. These features make them ideal for testing and measuring a wide range of electronic components and automotive devices.
Differences Between Bipolar Power Supplies and Other Multi-Polarity Units
While several power supply types offer positive and negative output capabilities, Matsusada Precision categorizes them based on operation and signal generation:
Bipolar Amplifier (Low-Voltage Amplifier): A four-quadrant power supply requiring an external signal input (no built-in function generator). See our Bipolar Amplifiers.
High-Voltage Amplifier: A high-voltage four-quadrant power supply requiring an external signal input. See our High-Voltage Amplifiers.
Reversible DC Power Supply: A unit that switches polarity between positive and negative (not continuous through zero). Examples include the EJ Series and CZE Series.
Dual Output Power Supply: Units providing separate positive and negative outputs simultaneously. These are often used for applications such as electrostatic chucks.