An electrostatic precipitator (ESP) is a device that electrically collects airborne dust by imparting a negative charge to the particles and attracting them to a positively charged collecting electrode.
The electrostatic precipitator is effectively used in industrial processes. At manufacturing sites, it is crucial to collect dust generated by industrial processes and other factors to prevent it from remaining suspended in the air and to maintain a clean environment.
For example, in factories that handle textiles or cut wood or resin, dust is collected to clean the air in the factory to solve environmental, health, and safety problems. Electrostatic precipitators are available in many variations to meet diverse needs.
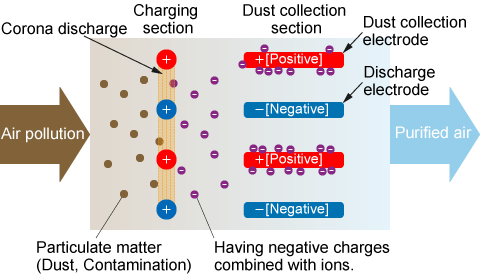
The electrostatic precipitator mechanism is simple. When high voltage is applied between the two poles installed in an electrostatic precipitator, the discharge electrode and the collecting electrode, corona discharge occurs between the electrodes, generating negative ions. These negative ions attach to the dust particles in the air, causing them to become negatively charged. The dust is then attracted to the collecting electrodes, which have a positive charge, and the dust in the air is collected.
An electrostatic precipitator requires a high-voltage power supply, typically in the range of tens to hundreds of kV, to generate the necessary corona discharge. Matsusada Precision's high-voltage power supplies are ideal for these applications. Our AU series and AUH series, for example, offer high power efficiency and a wide range of models suitable for this purpose.
- Related Terms:
-
- Electrostatic precipitator
- Contamination
- dust




