An open-collector output on a power supply is a type of digital output circuit used to signal the unit's status and other information. Open-collector circuits can also be used for inputs, allowing external control of functions like turning the output ON/OFF.
The open collector output connects an external circuit to the collector and emitter terminals of the transistor inside the power supply. There are two types of transistors, NPN and PNP type, and their usage differs. It is important to note which transistor type is used in the internal circuit.
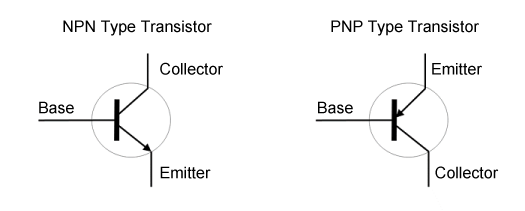
Difference between NPN and PNP transistors
Most of Matsusada Precision's power supplies use an NPN open-collector output for the status output of the analog remote control terminal.
For example,
When the status signal is active (asserted), the internal NPN transistor turns ON. This connects the output pin to ground through a low impedance path, creating a low-level (logic "0") voltage state.
When the status signal is inactive (de-asserted), the transistor turns OFF. The output pin is now in a high-impedance state (floating). If an external pull-up resistor is used, the output voltage will be pulled to a high-level (logic "1").
Generally, it is used by connecting a power supply and a pull-up resistor to an external circuit and converting it to a signal of the required voltage.
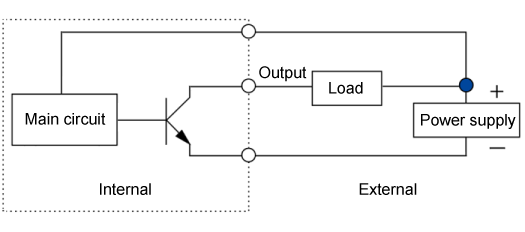
connection diagram of NPN open-collector output
For reference, a connection diagram of PNP open-collector output is shown below.
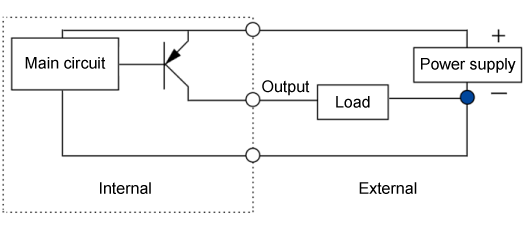
PNP open-collector output
To provide electrical isolation and enhance reliability, open-collector I/O circuits often use optocouplers (also known as photocouplers or opto-isolators). This isolation protects the power supply's internal control logic from external electrical noise, ground loops, and potential damage.
The NPN type is widely used for sensors and PLC outputs in the U.S. and Japan. In Europe, the PNP (sourcing) type is more common, as it can offer fail-safe behavior in certain scenarios, such as a short-to-ground.
The input/output logic circuit method may be transistor-transistor logic (TTL) or CMOS, in addition to the open-collector type.
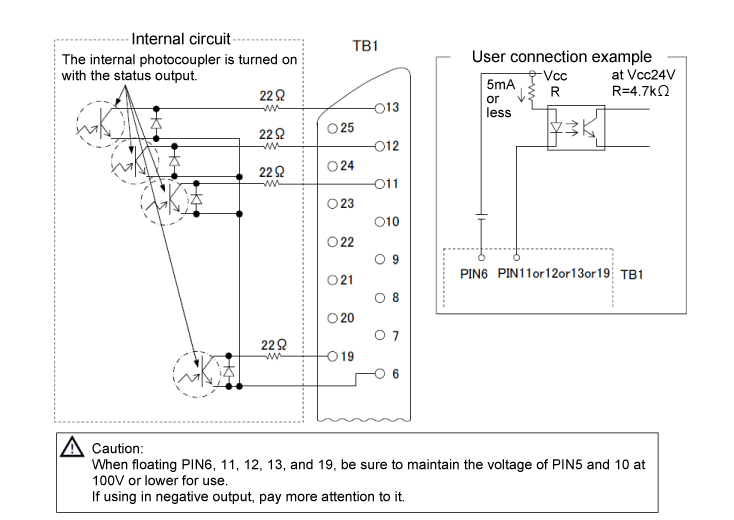
Power supply analog remote control internal circuit example


