An actuator is a mechanical element that is made up of mechanical and electrical circuits that convert input energy or electrical signals that are output from a computer into physical motion. This is called active operation or active drive.
The Matsusada Precision piezo actuator is a product that applies the characteristics of piezoelectric elements (extremely minute changes in elongation in the nanometer range, due to changes in applied voltage).
What Is Piezo?
A piezoelectric body is a material that has a positive piezoelectric effect that generates an electric charge when force or strain is applied to its crystal and an inverse piezoelectric effect that generates force or strain when an electric field is applied. Piezoelectric elements use the inverse piezoelectric effect of these materials. One such material that is used is lead zirconate titanate (Pb(Zr, Ti)O3).
Piezo Characteristics
Infinite resolution
By changing the applied voltage, the change in length of a piezo element appears as an extremely minute change in elongation in the nanometer range. Small changes in the applied voltage are converted into smooth motion, and there is no threshold voltage to impede this continuous movement. Therefore, the resolution is determined by the resolution (accuracy) of the applied voltage.
Piezo actuators do not have mechanical motion mechanisms such as gears. The elongation is based merely on the distortion of solid physical properties, and generally, there is no wear or deterioration. The results of durability testing showed no change even after several million cycles of elongation.
Large load bearing capacity
Piezo actuators are an optimal choice for positioning that requires micron and submicron precision. They can withstand loads of up to 5 tons, and can be used for positioning with ultra-high precision at a range of several hundred microns.
Fast responsiveness
In many cases, the speed of positioning movement has a very important meaning. Piezo actuators are positioning elements with faster responsiveness than any other actuator. The elongation speed depends on the speed of sound in the ceramic material, and acceleration that is several thousand times the gravitational acceleration is possible.
General Piezo Characteristics
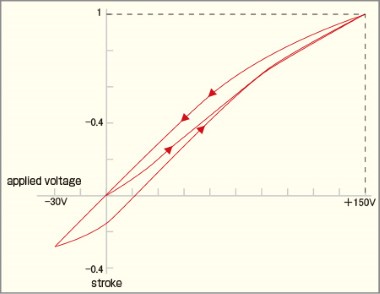
Hysteresis
The biggest disadvantage of piezo actuators is hysteresis. In other words, the elongation of a piezo actuator is not strictly proportional to the strength of the electric field. The voltage/stroke trajectory is represented as a nonlinear "hysteresis curve". When voltage is applied, the degree of elongation of the element depends on the size of the voltage. The maximum width of the hysteresis curve reaches 15% of the maximum stroke. In order to compensate for this, it is necessary to provide a highly accurate position detection mechanism (such as a strain gauge) externally.
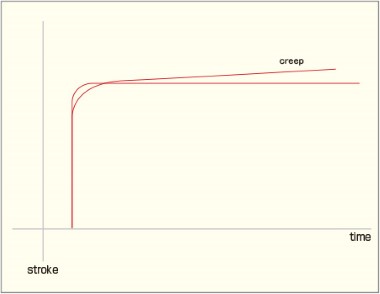
Creep
When the applied voltage of a piezo actuator is set to a new value, moderate elongation is observed until the actuator settles to that value. This extra elongation is closely related to hysteresis, and it is caused by the continued polarization of ceramics. This phenomenon is called creep phenomenon. The creep phenomenon is very small, and decreases exponentially.
Handling Precautions
Piezo actuators have a structurally robust design. However, the ceramic material is very fragile, and should be handled with care during installation.
Stacked piezo actuators can apply stress only in the axial direction.
Care is required to avoid applying biased force, shear stress, and tension.
For models with taps at the tip, care should be taken to avoid applying a rotational moment to the piezo body.
Stacked piezo actuators are made up of several layers. It is possible for these layers to become peeled off.
When installing an actuator between two opposing parallel planes, be sure to install the unit so that it is vertical to each face.
If the two surfaces are not parallel, use an actuator with an optional ball on the tip.
If the actuator has preliminary load functionality, it also covers slight deviations in the tension/installation state.
Related Technical Articles
Recommended products
Matsusada Precision provides precision control solutions with piezo actuators and piezo drivers.







